Anatomy- SPA forearm and hand Flashcards
palmar carpal ligament
palmar carpal ligament
the cubital fossa
most major structures pass through hereand into the hand via the carpal tunnel
Lateral intermuscular septum
a membrane that passes from the anterior border of the radius to the deep fascia surrounding the limb
ID This structure flexor retinaculum

flexor retinaculum
ID this structure


Name the 4 compartments of the hand
hypothenar
thenar
adductor
central

ID the things that run in each of the compartments of the hand
hypothenar: hypothenar muscles
thenar: thenar muscles
adductor: adductor pollicus
central: the flexor tendons, lumbricals, the superficial palmar arterial arch and the digital nerves and vessels.
What is the midpalm space and the significance?
midpalmarspaceis deep to the central compartment.
It is continuous with the anterior compartment of the forearm via the carpal tunnel
This is important because Infections of the hand may travel through the midpalmarspace into the forearm.
Identify the 4 thenar muscles
- Abductor pollicis brevis (APB)
- Flexor pollicis brevis (FPB)
- Opponens pollicis (OP)
- Adductor pollicis (AP)
Whata are the Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand (Medial to Lateral)
All For One And One For All
(Abductor digiti minimi, Flexor digiti minimi, Opponens digiti minimi, Adductor pollicis, Opponens pollicis, Flexor pollicis brevis, Abductor pollicis brevis)
Identify this muscle as well as its:
origin
insertion
action
innervation
Blood supply

Adductor pollicis (AP)
Orgin: Oblique head: 2nd and 3rd metacarpals
Transverse head: 3rd metacarpal
Insertion: thumb
Action: adduction and medial rotation of thumb
Innervation : Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8 and T1) (C8, T1)
Arterial Supply: Deep palmar arterial arch
Identify this muscle as well as its:
origin
insertion
action
innervation
Blood supply
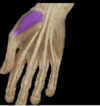
Abductor Pollicis Brevis (APB)
•Origin: Flexor retinaculum and tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium
•Insertion: thumb (1st metacarpal)
•Action: Abducts thumb
•Innervation: Recurrent branch of median nerve (C8 and T1) (C8, T1)
•Arterial Supply: Superficial palmar branch of the radial artery
Identify this muscle as well as its:
origin
insertion
action
innervation
Blood supply

Flexor pollicis brevis (FPB)
•Origin : radius and interosseous membrane
•Insertion : thumb
•Action: Extends proximal phalanx of thumb at carpometacarpal joint
•Innervation: Recurrent branch of median nerve,
Posterior interosseous nerve (C7 and C8), the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve(deep head)
•Arterial Supply Posterior interosseous artery
Identify this muscle as well as its:
origin
insertion
action
innervation
Blood supply
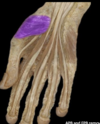
Opponens pollicis
Origin: Flexor retinaculum and tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium
•Insertion: Lateral side of 1st metacarpal
•Action: Draws 1st metacarpal laterally to oppose thumb toward center of palm and rotates it medially
•Innervation: Recurrent branch of median nerve (C8 and T1) (C8, T1)
•Arterial Supply: Superficial palmar branch of the radial artery
Identify the 4 hypothenar muscles
- Abductor digitiminimi(ADM)
- Flexor digitiminimibrevis (FDMB)
- Opponensdigitiminimi(ODM)
- palmarisbrevis
Identify this muscle as well as its:
origin
insertion
action
innervation
Blood supply

Abductor digiti minimi(ADM)
-Origin : Pisiform
-Insertion: pinky
-Action : flexion and abduction of pinky, extension of PIP and DIP joints
-Innervation : Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8 and T1) (C8, T1)
-Arterial Supply : Ulnar artery
Identify this muscle as well as its:
origin
insertion
action
innervation
Blood supply

Flexor digiti minimi brevis (FDMB)
Origin: Hook of hamate and flexor retinaculum
Insertion: pinky
Action: flexes the MCP joint of pinky
Innervation: Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8 and T1) (C8, T1)
Arterial Supply: Ulnar artery
Identify this muscle as well as its:
origin
insertion
action
innervation
Blood supply

Opponens digiti minimi
-Origin Hook of hamate and flexor retinaculum
-Insertion pinky
-Action opposition ( draws metacarpal in palmar direction)
-Innervation Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8 and T1)
-Arterial Supply Ulnar artery
Identify this muscle as well as its:
origin
insertion
action
innervation
Blood supply
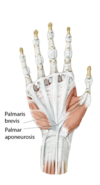
Palmaris Brevis
-Origin palmar aponeurosis
-Insertion skin of hypothenar eminance
-Action depends the cup of the palm and helps to grasp objects, tightens the palmar aponeurosis (protective)
-Innervation ulnar nerve
-Arterial Supply
what is unique about lumbricals and what are they innervated by

they connect to tensons instead of bone
1 and 2- median nerve
3 and 4- ulnar nerve
where do lumbricals originate
radial side of FDP tendon and insert on dorsal side of extensor expansions
O: flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)
I: extensor expansions of digits 2-5
innervated by the median nerve for 2 and 3 and by ulnar for 4 and 5
MCP joint: flexion
PIP and DIP: extension
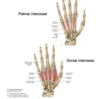
what are the two groups of muscles found between the metacarpals
3 palmar interossei
- PAD –> adduct the hand
4 dorsal interossei
- DAB –> abduct the hand
Identify this muscle as well as its:
origin
insertion
action
innervation
Blood supply

Palmar interossei (3)
•Origin Palmar 1 - 3: Palmar surfaces of 2nd, 4th and 5th metacarpals (unipennate muscles)
•Insertion Palmar 1 - 3: Extensor expansions of digits and bases of proximal phalanges of digits 2, 4 and 5
•Action Palmar 1 - 3: MCP joint flexion, PIP and DIP extension and adduction toward third finger
•Innervation Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8 and T1) (C8, T1)
•Arterial Supply: Palmar metacarpal arteries
Identify this muscle as well as its:
origin
insertion
action
innervation
Blood supply

Dorsal interossei
Origin Dorsal 1 - 4: Adjacent sides of two metacarpals (bipennate muscles)
•Insertion Dorsal 1 - 4: Extensor expansions and bases of proximal phalanges of digits 2 - 4
•Action Dorsal 1 - 4: MCP joint: flexion, PIP and DIP extension and abduction from 3rd finger
•Innervation Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8 and T1) (C8, T1)
•Arterial Supply Dorsal 1 - 4: Dorsal and palmar metacarpal arteries














