anatomy- neurovasculature Flashcards
what borders the axillary branches
1st rib and teres major, pec minor marks the 2nd part of the axilary (remmeber part 1 has 1 artery, 2 has 2 and 3 has 3)
1- superior thoracic
2- thoracoacromial and lateral thoracic
3- anterior and posterior circumflex, subscapular
(subscap branches into the thoracodorsal and the circumflex artery)
what does the brachial artery travel with
what does the deep brachial arery travel with
superior ulnar collateral artery
median nerve
radial nerve
ulnar nerve
describe the flow through the brachial artery
brachial artery is the majory artery and is the one measured with BP
brachial artery terminates at the cubita fossa where is then branches into the radial and ulnar arteries
Major branches:
①Deep brachial artery (profunda brachii artery)
- Descends posteriorly and branches into the radial and middle collateral aa, which anastomose with the radial recurrentand interosseous recurrent aa, respectively
- Will also anastomose with the PHC and AHC.
②Superior ulnar collateral artery
posterior to the medial epicondyle;
anastomoses with the posterior ulnar recurrenta.
③Inferior ulnar collateral artery
•Descends anterior to medial epicondyle and provides an anastomoses with the anterior ulnar recurrenta
what is the most common place to take a BP
The most common place to take a pulse is at the radial artery just proximal to the thumb. The artery is found lateral to the tendon of the FCR
course of the radial artery
1.Radial Artery
- Gives off the radial recurrent artery before passing over the insertion of pronator teres.
- Descends the forearm supplying the lateral forearm muscles.
2.Passes through the thenar muscles to form the superficialpalmarbranch and arch.
course of the ulnar artery
- Larger of the two terminal branches, it travels under the deep head of pronator teres to give rise to the anterior & posterior ulnar recurrent arteries, which anastomose with the inferior and superior ulnar collateral arteries, respectively.
- Gives rise to the common interosseous artery, which then divides into:
- Anterior interosseous artery that course with the posterior interosseous artery
4 .Branches into superficial palmar carpal arch and deep palmar arch.
*** if ulnar artery branches before cubita fossa it will run superficial
what does the posterior interosseous supply
superficial extensor muscles
what does the ulna artery supply
the medial forearm muscles
where does the ulnar artery enter the hand
the ulnar canal between the pisiform and hamate
What does the ulnar artery branch into
a large superficial palmar archand a smaller deep palmer arch
superfical palmar- common palmar- deep palmar metacarpal arteries of radial artry
The superficial palmar arch gives rise to three common palmar (digital) arteries that lie on the 2nd, 3rdand 4thlumbricals.
The common palmar arteries anastomose with the palmar metacarpal arteries from the deep palmar arch of the radial artery.
what supplies the sides to digits 2-4
two proper palmar digital arteries from the common palmar
what are the ways that the median nerve can be injured
- carpal tunnel syndrome
- Severed in elbow region (loss of flexion of PIP joints of all digits; loss of flexion of DIP joints of digits 2-3).
- Compression near the elbow within the 2 heads of pronator teres.
- Proximal to flexor retinaculum (suicide attempts where wrists are slashed).
what is the signifiance of the ulnar nerve
wha
principal nerve of the hand
branches- palmar cutaneous & dorsal cutaneous
ID these arteries

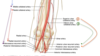
what is the volar aspect of the hand
palm










