Anatomy of the shoulder and pectoral region Flashcards
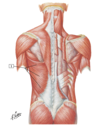
Rotator cuff muscle
SITS S: supraspinatus I: Infraspinatus T: teres minor S: subscapular
supraspinatus innervation
suprascapular nerve
subclavius action
anchors and depresses clavicle
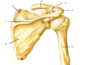
label the following:

- Pactoralis major
- Clavicle
- Sternal end of clavicle
- Acromial end of clavicle
- Acromion
- Coracoid process
- Lesser tuberosity of humerus
- Bicipital groove
- Greater tuberosity of the humerus
- Cephalic vein
latissimus dorsi innervation
thoracodorsal nerve
Name the muscle:

Pectoralis major
Origin (proximal attachment): clavicle, superior six costal cartilages.
Insertion (distal attachment): Intertuberculargroove of humerus.
trapezius action
rotate the scapula for full abduction, elevate the shoulder, retract the shoulder and draw scapula downward
levator scapulae action
elevates scapula and tilts its glenoid cavity inferiorly by rotating scapula
ROTATOR CUFF MUSCLE SUPPORTS THE SHOULDER JOINT The inferior part of the joint capsule, the only part not reinforced by the rotator cuff muscles, is its weakest area
xxxx
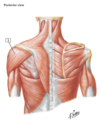
Name the muscle

DELTOID
Origin: lateral third of clavicle, superior surface of the acromion, and spine of the scapula.
Insertion: deltoid tuberosity
common site for humerus fracture
surgical neck
the glenoid cavity is deepened by the
fibrocartilaginous glenoid labrum and accepts little more than a 1/3 of the humeral head.
Name the muscle
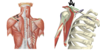
TRAPEZIUS
Origin: external occipital protuberance, superior nuchal line of occipital bone, ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes C7 & T1-T12.
Insertion: posterior border of the lateral third of clavicle, acromion and scapular spine.
latissimus dorsi action
extend, adduct, and medially rotates the humerus
Name the muscle

RHOMBOID MINOR AND MAJOR
Origin: spinous processes of C7 –T5
Insertion: medial border of scapula.
nerve supply of acromioclavicular joint
lateral pectoral and axillary nerves
which is more serious anterior or posterior dislocation of the clavicle?
posterior dislocation is more dangerous since it compresses the vessels
Name the muscle

SUPRASPINATUS
Origin : supraspinatus fossa
Insertion: greater tubercle.
subscapular action
medially rotate and adduct arm
teres minor innervation
axillary
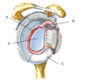
Label the following:

- Acromion
- Anatomical neck
- Clavicle
- Coracoid process of scapula
- Glenoid fossa
- Greater tubercle
- Head of humerus
- Lesser tubercle
- Scapula
- Surgical neck

subscapular innervation
upper and lower subscapular
Arm
From shoulder joint to elbow
Pectoral girdle
is a bony ring, incomplete posteriorly, formed by the scapular and clavicle and completed anteriorly by the manubrium of the sternum
rhomboid major and minor function
retract scapula and rotate it to depress glenoid cavity, fix scapula to thoracic wall
blood supply of acromioclavicular joint
suprascapular and thoracoacromial arteries
pectoralis major Innervation
lateral &medial pectoral nerves
rhomboid major and minor innervation
dorsal scapular nerve
How can you dislocate the acromioclavicular joint ?
falling laterally on shoulder
Name the muscles

Rotator cuff muscles
SITS

axioappendicular muscle consists of (anterior) (4)
- pectoralis major 2. pectoralis minor 3. subclavius 4. serratus anterior
serratus anterior action
protracts scapula and holds it against thoracic wall, rotates scapula. Called BOXER’S muscle
Clavicle
transmits shocks from the UL to the axial skeleton
Name the muscle

TERES MAJOR
Origin:scapula
Insertion: intertubercular groove of humerus.
deltoid action
abduct the arm with supraspinatus, medial and lateral rotation
nerve supply by sternoclavicular joint
supraclavicular nerve and nerve to subclavius
What is shoulder separation?
dislocation & lesion of AC
Name the muscle

LEVATOR SCAPULAE
Origin: posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C1-C4 vertebrae.
Insertion: medial border of scapula superior to root of spine.
Identify each condition:
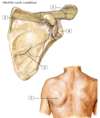
- Acromial fracture
- Coracoid process fracture
- Scapular body fracture
- Glenoid fracture
- Scapular winging