Anatomy of hand Flashcards
Palmar branch of both the median and ulnar Travels Superficial to the ______ _________ this portion of the median nerve usually remains functioning during carpal tunnel syndrome
flexor retinaculum
The radial nerve: superficial branch to dorsal aspect of the
proximal 3 ½ lateral fingers (to about middle phalanges)
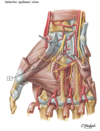
The median nerve supplies the
proper palmar digital nerves to distal 3 ½ lateral fingers
The ulnar nerve supplies the
Dorsal branch of the ulnar nerve: emerges from under the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon, on the medial aspect of the distal forearm, and winds around the wrist to provide cutaneous innervation to the dorsal aspect of the 1½ medial fingers
Recall that the cephalic vein originates from the lateral aspect and the ______ from the medial aspect of the dorsal venous arch
basilic
Median cubital vein joins the _______ vein to the basilic vein in the superficial fascia of the cubital fossa.
cephalic
lymphatics: Lateral side: empty into the __________ which then drain to the apical nodes of the axilla
infraclavicular nodes
lymphatics: Medial side of the hand and forearm can drain directly into the
lateral group of axillary nodes or to the cubital (supratrochlear) nodes before draining in the lateral group of nodes.
Dupuytren’s Contracture
Is a localized thickening and contracture of the palmar aponeurosis. •A condition in which the medial part of the palmar aponeurosis undergoes progressive shortening •It commonly starts near the root of the ring finger and draws that finger into the palm, flexing it at the metacarpophalangeal joint. •Later, the condition involves the little finger in the same manner. •In long standing cases, the pull on the fibrous sheaths of these fingers (little and ring) results in flexion deformity of the proximal interphalangeal joints . •The distal interphalangeal joints are not involved and are actually extended by the pressure of the fingers against the palm. •Surgical division of the shortened part of the aponeurosis is done to straighten the bent fingers
Attachments of Flexor retinaculum
Medially: hook of the hamate & pisiform bones, but volar carpal ligament encloses ulnar nerve and vessels. Laterally: to scaphoid & trapezium, but splits to enclose tendon of flexor carpi radialis tendon
Structures passing superficial to Flexor retinaculum:
Ulnar nerve & vessels, palmaris longus tendon, palmar cutaneous branch of median and ulnar nerves, superficial palmar branch of radial artery
Structures passing deep to Flexor retinaculum:
Median nerve, tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus with ulnar bursa, tendon of flexor pollicis longus with radial bursa.
Extrinsic muscles are responsible for _____ movements of hand
crude
intrinsic muscles control ____ movements of hand
fine
Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand
-Thenar (thumb) -Hypothenar (little finger) muscles -Interossei muscles (four dorsally and three anteriorly) originating between the metacarpal bones -Lumbrical muscles arising from the deep flexor (and are special because they have no bony origin) to insert on the dorsal extensor hood mechanism.
Thenar Eminence (Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand)
- Abductor pollicis brevis - Flexor pollicis brevis - Opponens pollicis brevis All these muscles act on the thumb. They are all supplied by the median nerve
Hypothenar Eminence (Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand)
- Abductor digiti minimi - Flexor digiti minimi - Opponens digiti minimi All act on little finger They are supplied by ulnar nerve
Lumbricals (Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand)
• Each lumbrical tendon inserts on the lateral side of the corresponding extensor (dorsal digital) expansion (on the dorsal aspect of the MCP joint). • First 2 lumbricals have one head whereas the 3rd and the 4th have 2 heads •Flex the MP joints and extend the IP joints. •1st and the 2nd are supplied by the median nerve, 3rd and 4th are supplied by the ulnar nerve.
Dorsal Interossei (Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand)
- bipennate - 4 dorsal and are numbered from lateral to medial side - Abduct the index, middle and ring fingers ( DAB), also flex the MP joints and extend the IP joints of these 3 fingers. - Innervated by ulnar nerve.
Palmar Interossei (Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand)
- unipennate - Are 4 (sometimes 3), numbered from lateral to medial side. -Adduct the index, ring and little fingers (PAD), also flex the MCP joints and extend the IP joints of these 3 fingers. - Innervated by ulnar nerve.
Superficial palmar arch: Formed by (Palmar Arches Deep & Superficial)
superficial branches of ulnar (2/3 rd ) and radial arteries (1/3 rd)
Deep arch: Formed by (Palmar Arches Deep & Superficial)
deep branches of radial (2/3rd and ulnar arteries (1/3 rd)
The superficial arch is very superficial, just deep to the __________ (Palmar Arches Deep & Superficial)
palmar aponeurosis.
Laceration of palm can cause severe bleeding. -Bleeding can be controlled by clamping (Palmar Arches Deep & Superficial)
the brachial artery against humerus, not by compressing the radial or ulnar or both arteries (because of connection between palmar & dorsal arches)