Anatomy of Bloodflow Through Fetal Heart Flashcards
what are the black arrows

valve flaps of the atrio-ventricular or tricuspid valve
what are the red and pink arrows
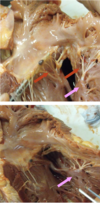
red: chordea tendineae of tricuspid valve
pink: papillary muscles
what is the structure of the right AV (tricuspid) valve

3 cusps: chordae tendineae and papillary muscles/fibrous annular ring support

what is the action of the AV valve
passive/prevents backflow of blood into atrium at systole
1st heart sound lub = closure of right and left AV valves
what are the structures of the right ventricle


list 5 anatomical features of the right ventricle
- wall: endocardium, myocardium and epicardium
- trabecular septomarginalis: distinct feature of right atrium –> carries the short circuiting impulse to the walls –> related to the papillary muscles which will contract before the walls of the heart contract to prepare to hold the valves
- trabecular carneae: elevation of wall –> act like pectinate muscle –> dampen out the turbulence of blood
- pulmonary trunk exits RV on the left lateral side of the heart
- walls are smooth and shiny
what are the structures (transverse section through R&L ventricles)

- most cranial point
- right ventricle
- interventricular septum
- left ventricle
identify the labels and describe how blood flows through the right side

right ventricle forms the cranial margin of heart
blood exits RV through pulmonary trunk (on left lateral side) through pulmonary semi-lunar valve
pulmonary trunk bifurcates into L&R pulmonary arteries which enter root of L&R lung

list the anatomical features of the pulmonary semilunar valve

- at junction of RV and pulmonary trunk
- second heart sound ‘dub’ = closure of pulmonary and aortic semi lunar valves

what is the ligamentum arteriosum
ligament linking the pulmonary trunk and aorta
fetal remnant of the ductus arteriosus
what are these structures


describe the blood flow through the left side of the heart
- oxygenated blood enters left atrium (& auricle) from the lungs via pulmonary veins –> mitral valve (bicuspid) or left AV valve –> left ventricle –> aortic semi-lunar valve guards entrance to aorta –> aorta exits middle of base of heart
what ventricle forms the base of the heart
left –> very thick wall
what are the anatomical features of the mitral valve
2 cusps
what are the structures of left atrium and ventricle


what are the structures (dorsal view of heart after removal of atria)

- right atrioventricular valve
- left atrioventricular valve
- aortic valve
- pulmonary valve
- left coronary artery
- righ coronary artery
cr: cranial

what are the structures
A: mitral valve
B: semi-lunar valve
C: coronary circulation

what is the puncta maxima
points on the chest wall where heart sounds are heard best
left thorax: between 3,4,5th intercostal space
right thorax: tricuspid 4th intercostal space
what are the structures of the thorax

- cranial extent of heart
- caudal extend of heart
- basal border of lung
- line of pleural reflection
- caudal border of lung percussion area shown on right side
what are the structures shown here

- right auricle
- left atrium
- left atrioventricular valve
- interventricular septum
- aorta
what are the structures of the early fetal heart

placenta –> maternal and fetal blood flow coming close to each other
the umbilical vein has nutritious and highly oxygenated blood
returns deoxygenated blood to the placenta

what is the 1st step in the formation of the 4 chambered heart
subdivision of the channel between the primitive atrium and ventricle
2 chambered heart recieving and distributing areas that is segmented in the middle –> partitions coming from above and below

what is the second step in the formation of the 4 chambered heart
subdivision of the primitive ventricle continues –> interventricular septum
the atrioventricular channel splits into two-av canal cushions
the interatrial septum starts to form but is never complete

what is the third step in the formation of the 4 chambered heart
ventricles are now separate
AV valves form
the atria continue to intercommunicate (RA to LA) via foramen ovale






