Anatomy Flashcards
1? 2?

5? 6? 7?


1? 2? 3?


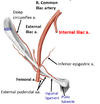
Green arrow?

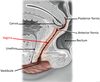
Postganglionic sympathetic fibers (they synapsed in the ganglion) leaving the sympathetic chain and joining a sacral nerve (S1). Will leave the pelvis with to go to the legs to nnervates blood vessels, sweat glands, hair follicules, etc.
Where are the 3 potential sites of obstruction of the ureters in case of kidney stones?
- at the junction of the ureters and the renal pelvis
- where the ureters cross the brim of the pelvic inlet
- during their passage through the wall of the bladder

3? 4?
3? 4? 5?


Red arrow?

Sacral splanchnic nerves - Preganglionic sympathetic fibers (they came down the chain) which will synapse in the inferior hypogastric plexus. They provide sympathetic innervation to the pelvic organs.


4? 5?

7? 8?


3? 4?


1? 2?


1? 2? 3?


1? 2?

1? 2?


3? 4?

3: Crus
4: Bulb of the vestibule
4? 5? 6?

4? 5?


3? 4?


1? 2?


25? 26?


5? 6?


9? 10? 11? 12?


1?


5? 6?
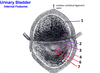
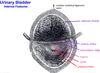
The fornices are part of which organ?
the VAGINA, not the uterus
9? 10?


3? 4? 5?


13? 14?
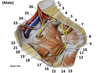
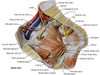
1? 2? 3?


9? 10?


1? 2?


3? 4?


4? 5?


What are uterus fibroids?
- They are the most common tumours of the female genital tract.
- 40% of women by the age of 40 have them
- Noncancerous (benign) growths that develop in the muscular wall of the uterus
- They do not always cause symptoms, but their size and location can cause pain and heavy bleeding
- They may be genetic predisposition;
- They range greatly in size from very tiny (a quarter of an inch) to larger than a cantaloupe (10 inches or more).
- In most cases, there is more than one fibroid in the uterus.
23? 24?


7? 8?

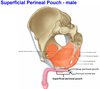
If there’s a perforation on the penis and the urethra and it cuts through buck’s fascia, where can you expect to find urine?
Anterior abdominal wall AND the scrotum
1? 2? 3?

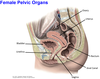
1? 2?


1? 2?


4? 5? 6?


7? 8? 9?

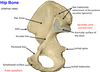
4? 5?


1? 2? 3?

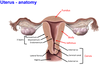
7? 8?


1? 2?


1? 4? 5?


3? 4?


1? 2?


1? 2? 3?


5? 6?


3? 4?


What structures can you find in the female superficial perineal pouch?
- Greater vestibular gland
- Perineal vessels and nerves
- Pudendal nerve
- Superficial transverse perineal muscle
- Ischiocavernosus muscle
- Bulbospongious muscle
- Crus of the clitoris
3? 4?


1? 2? 3?
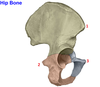

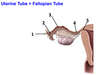
Where do most ectopic pregnancies appear?
In the Fallopian tubes
4? 5?


4? 5?

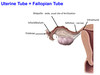
1? 2?

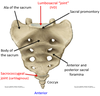
1? 2? 3?


1? 2?


1? 2? 3?


5? 6?
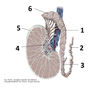

19? 20?
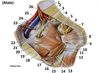

1? 2?

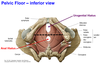
4? 5? 6?


1? 2? 3?


4? 5?


1? 2? 3?


What structures can you find in the male deep perineal pouch?
- Bulbourethral gland or Cowper’s gland
- Perineal vessels and nerves
- Urethra (membranous part)
- Deep transverse perineal muscle
- External urethral sphincter muscle
4? 5? 6?
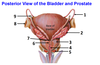
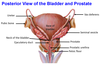
4? 5?


1? 2?
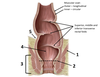

2? 3?


1? 2?


3? 4?


15? 16?


1? 2? 3?


1? 2? 3?

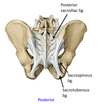
1?


11? 12? 13?


11? 12?


1? 2? 2?


3? 4?


1? 2?


3? 4?
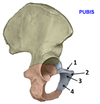

1? 2?

1: Ischiocavernosus muscle
2: Bulbospongious muscle
1? 2?

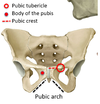
3? 4?


5? 6?


9? 10? 11?


11? 12?


3? 4?
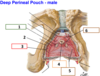

5? 6? 7?


What structures can you find in the male superficial perineal pouch?
- Ischiocavernous muscle
- Bulbospongious muscle
- Crus of the penis
- Bulb of the penis
- Perineal vessels and nerves
- Internal pudendal artery and vein
1? 2?


21? 22?


1? 2?

1? 2?


1? 2? 3?

7? 8?

5? 6?


3? 4?


9? 10?


3? 4? 5? 6?


3? 4?

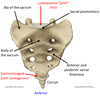
5? 6?


1?


1? 2? 3?


What structure is a remnant of the embryonic uterovaginal canal in males?
The Prostatic utricle
5? 6?


5? 6?


1? 2?

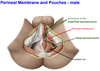
5?


5? 6?


7?
3? 4?


1? 2?

1? 2?


1? 2? 3?

1?
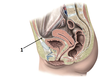
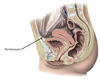
1? 2?


3? 4? 5?


5? 6?


4? 5? 6? 7?
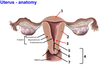
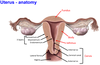
1? 2? 3?


1? 2?


1? 2?


1? 2?


1? 2? 3?

1? 2? 3?

1? 2?


3? 4?


1? 2?


1? 2?

3? 4?


7? 8? 9?


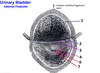
Which bladder sphincter is voluntary?
The EXTERNAL one.
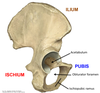
What are the gender-specific differences of the pelvis?
Male pelvis is narrow and tight, and female pelvis is pulled out a bit and is wider = advantageous for childbirth

5? 6?

3? 4? 5?
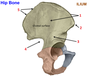

3? 4?


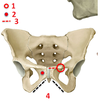
3? 4?
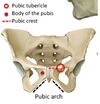
What structures can you find in the female Deep perineal pouch?
- Urethra (proximal part)
- External urethral sphincter muscle
- Deep transverse perineal muscle
- Perineal vessels and nerves
- Vagina
Violet arrow?

Pelvic splanchnic nerves - Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers (came out the sacral foramen with the sacral nerve) which will enter the inferior hypogastric plexus but pass right through it. They will synapse in the walls of the organs. They provide parasympathetic innervation to the pelvic organs.
1? 2? 3?

1: Ischiocavernosus muscle
2: Bulbospongious muscle
3: Crus
3?


1? 2? 3?


17? 18?

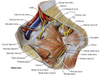
1? 2?


1? 2? 3?
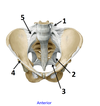

1? 2?

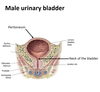
5? 6?


5? 6?

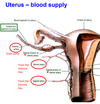
1? (at the bottom of the picture)


3? 4?

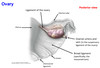
What are the functions of the uterine (Fallopian) tubes?
- transports eggs from ovary to uterus
- site of fertilization of eggs by sperm
- transports dividing zygote to uterine cavity
- provides nourishment for the zygote
1?

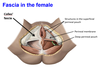
1? 2?

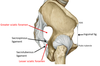
7? 8?


1? 2?


3? 4?


1? 2?

1: Rectum
2: Uterus
1?
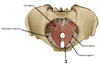

5? 6?


2? 3?

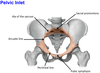
3? 4? 5?


6? 7?


2?


1?

5? 6?

3? 4? 5?

7? 8?


7? 8?


1? 2?


3? 4?


3? 4?

7? 8?




