Acquired Immune Deficiency and Headache Flashcards
Cryptococcus ________ is a cause of ________ in immunocompromised problems
Cryptococcus neoformans is a cause of meningitis in immunocompromised problems.
Almost all AIDs patients get a bout of ___________ that cause dysphagia
Almost all AIDs patients get a bout of candida albicans that cause dysphagia

You get a range of infections/ disease with AIDs, what is interesting about these?

They are from normally very rare, uncommon diseases.
But, when our CD4 count drops to a level that low, our normal immune response cannot do what it usually would.
Note especially the fungal infections.
People get a succession of illnesses that occur as the CD4 continues to drop, until they eventually die of one of the illnesses.

What are Fugal Infections?
Common, minor skin and mucosal infections and rare, serious deep tissue infections.
Fungi are either Yeasts (look like bacteria) or Moulds
Describe the structure and example of Yeast and mould Fungi?
Yeasts:
- round or oval, reproduce by budding
- -Candida albicans* and other candida sp.
- -Crytococcus neoformans*
Moulds: (without the outer layer)
- tubular hyphae, reproduce by spores, that originate in the ‘roots’
- dermatophytes
- Aspergillus species
- zygomycetes

What is the most important yeast in regards to AIDs, an what does it do?
Candida albicans
- Commensal of mouth, gut, vagina
- Overgrowth related to antibacterial therapy, immune supresion, hormonal effects and foreign bodies
- only takes a minor change in the balance of these to allow this to multiple in colonies on the mucosa
- you can scrap off, and wont have fever etc, it’s just surface
- children as ‘nappy rash’ or under folds of fat
Causes:
- oral or vaginal “thrush”
- Cutaneous or nail candidiasis less common!
- urinary catheter-related bladder infection les common

Lab diagnosis of Candida albicans?
It is seen as yeasts with pseudo-hyphae on Gram Stain
It grows well on Blood agar.
Non-invasive and the patient would not show sigs of fever etc.

After taking a mouth swab and the lab results show Candida albicans, what does this mean and what treatment should be done??
This means they have a yeast infections/colonisation (oral thrush) of the mouth. This can be treated with an antifungal agent and their dysphagia resolves within a few days.
BUT this will be frequently occuring!
- Usually topical, sometime oral
- nystatin suspension or pastilles
- amphotericin B pastilles
- azolle pessaries or cream
Other then Candida albicans, whats the “other” yeast that can cause issue in AIDs patients
Cryptococcus neoformans
- Usually present in the environments but not in humans
- C. neoformans var neofarmans → pigeon faeces
- C. neoformans var gatti → gatti
- Environmental contamination is common
How do you get an infection of C. neoformans
-
Pulmonary Infection
- due to inhalation of aerolised fungus from environment
- totally controlled in people with normal IS
- is usually asymptomatic
- Spread via blood to CSF: ONLY in people w severe immunodeficiency
- Menigitis in immunodeficient people eg; AIDs, high dose prolonged corticosteriod therapy etc
- Chronic Lymphocytic meningitis: slow deterioration in mental state with heache and fever. (unlike rapid bacterial meningitis)
How do you confrim a diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis?
- Usually there’s 10-100 (not 1000s) of WBC in CSF
- Lymphocytes not PMN predominance
- Protein raised, gluose
- Encapsulatedyeasts seen with India Ink stain, C.neoformans grown on agar
- Cryptococccal antigen +ve in CSF and serum

What are Dermophytes? (Moulds)
- cause tinea (ringworm), capitis, corporis, cruris, pedis etc
- “Never” are invasive (skin)
- Human or animal hosts
- Often have larger original lesion with many other subsequent
- onychomycosis (dried chalky nails due to an mould infection)
- Branching of mould in a lab swab.

Treatment of dermatophytes? (moulds)
For skin → a topical azole clotrimatozole, econazole
Antifungal drugs that work against yeasts AND moulds
For nails** → an oral agent (terbinafine 250mg daily, for 3-4months)
or ( itraconazole 400mg daily, for 1 wk in 4, for 3-4months)
Two common skin Fungal infections that we can get?
- Pityriasis versicolor : depigmenting rash (like rainfrops on the skin)
- Seborrhoeic dermatitis: dandruff of the face. Red greasy itchy rash
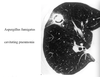
What is the rare, severe mould?
Asperillus fumigatus
- A spore bearing branching mould
- widespread in rotting vegetation
- a RARE cause of severe disease in neutropenic patients
- can also cause allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
- this is only in the immunocompromised, that leads to a large cavitating spore
- centre of infection is necrotic lung, with a halo of