Acne, Rosacea, and Related Disorders Flashcards
***What are the 4 factors that contribute the the Pathogenesis of Acne?
***Where is the source of acne?
LOCATION = PILOSEBACEOUS UNIT
Four Factors:
1. Sebaceous gland Hyperplasia
2. Abnormal follicular desquamation (skin clogs the pore)
3. Propionibacterium acnes colonizes
4. Inflammation
****What is the hair follicle called once it gets blocked?
• ****Is this an inflammatory Lesion?
• ****two types of blockage?
**MICROCOMEDO (1st step)
• Non-inflammatory lesion
2 Types of Microcomedo:
• Blackhead => OPEN
• Whitehead => CLOSED
What lesions follow the formation of a Microcomedo?
Inflammatory Lesions:
• Red: papules, pustules, nodules, cysts
We rate acne on the basis of (a)_____________ and (b)_____________. what are the subsets of these categories?
(a) MORPHOLOGY
• Comedonal
• Inflammatory
• Mixed => Majority of Acne
(b) SEVERITY
• Mild
• Moderate
• Severe
**site and presence of scarring or post-inflammatory hypo/hyperpigmentation (PIH), and erythema may also be taken into account***
What is shown here?
• are these lesions inflammatory or non-inflammatory?
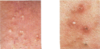
Left: Closed Comedones (whiteheads)
Right: Open Comedones (blackheads)
What is shown here?
• are these lesions inflammatory or non-inflammatory?

Left: Papules/Pustules
Right: Nodules
T or F: often acne is treated BOTH topically and systemically.
True
What Topical Tx is often used for acne?
OTC:
• Benzoyl Peroxide
• Salicylic acid
Prescription:
• Antimicrobials
• Retinoids
• Combination Products
What systemic Products are often used in the Tx of acne?
Systemic:
• Antibiotics
• OCPs
• Isotretinoin
What is the general use of Benzoyl peroxide and Salicylic acid in the treatment of acne?
• Which is most effective?
As monotreatments these are only good for very mild acne. Benzyoyl Peroxide is more effective than Salicylic acid
Benzoyl Peroxide:
• How does it work?
• Why do we use it adjunctively with abx?
• Side Effects?
MOA:
• Kills P. acnes
• Mild comedoLYTIC
• Mild-Antiinflammatory
Adjunctive Use:
• Limits the development of P. acnes antibiotic Resistance.
Side Effects:
• Irritation
• Bleaching
• ACD 1:500
What topical Abx are used in the Tx of acne?
• MOA?
• Side Effects?
Clindamycin and Erythromycin use in ACNE topically
MOA: Work as antibacterials AND anti-inflammatories
Both inhibit 50S bacterial subunit
Side Effects:
• Irritation
• C. Diff with Clindamycin possible
Why are TOPICAL ABX not recommended as monotherapy in Acne treatment?
Why no topical Clindamycin or Erythromycin as Topical Abx:
• SLOW ONSET
• RESISTANCE
• NOT COMEDOLYTIC (pts. won’t see instant results)
COMBINE these with Benzoyl Peroxide with works rapidly, prevents resistance, and is comedolytic
While Benzoyl Peroxide and Topical Abx are okay treatments, what is THE FIRST LINE THERAPY FOR ALL TYPES OF ACNE?
• why?
• Side effects?
TOPICAL RETINOIDS => 1st line therapy in ALL acne
WHY?
- *1. Normalizes Follicular Desquamation
2. Anti-inflammatory
3. Enhances penetration of other compounds**
Side Effects:
• local irritation
***What are the topical retinoids used in the treatment of acne?
• list them from strong to weak?
- ADAPALENE
- TRETINOIN
- TAZAROTENE (pregnancy category X)
When should you perscribe systemic antibiotics to a patient with Acne?
• what is your end goal?
- *Moderate - Severe Acne** should get systemic Abx.
- *• end goal it to get them off the abx. and on maintenance with topical therapy**
What are the 1st choices of Systemic Abx. to give patients with Acne? (which 1st line drug is the best)
• 2nd line drugs?
• what is the side effect profile of these drugs?
1st line systemic tx:
• DOXYCYCLINE (preferred)- lower side effects: photosenstivity an esophagitis (take with water)
- Minocycline: Dyspigmentation, lupus-like rxns, pseudoturmor cerebri, SJS, DHS
- Tetracycline: GI upset, TOOTH staining
2nd line systemic tx:
• Erythromycin- GI Upset
• Bactrime
Who benefits from the use of oral contraceptives in acne treatment?
Females with moderate to severe acne that flares with periods are good candidates
• Anti-androgen effect suppresses sebum production
What are the indications for the use of Oral Retinoids in the treatment of Acne?
• why is the oral use of this drug so effective?
SEVERE, SCARRING or REFRACTORY acne
WHY SO EFFECTIVE SYSTEMICALLY?
- Attacks ALL 4 phases of acne*
- *1. Decreases Sebaceous Gland Size (90% red.)
2. Normalizes Follicular Keratinization (prevents new comedones)
3. Inhibits P. acnes
4. Anti-inflammatory**
What side effects do we have to worry about in a patient that we are giving oral retinoids to?
DRYNESS RELATED SYMPTOMS
• lips, skin, eyes, nosebleeds
ACHES:
• Back, Muscle (athletes), head
SEVERE EFFECTS:
• Suicidal Ideation
• TERATOGENIC
• Skeletal Fractures
• Inflammatory Bowel Disease
How would you treat the following types of acne:
• Mild Comedonal
• Mild inflammatory/Mixed
• Moderate inflammatory/Mixed
• Severe inflammatory
Note: inflammatory just means they are starting to get papules and pustules

What would you give this patients for their acne?

This is severe mixed acne:
Minimal Scarring then:
• Topical Retinoid + topical antimicrobial + oral Abx
More Severe Scarring then:
• Isoretinoin
What would you give this patient for her acne?
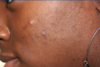
Mild Mixed Acne
Topical Retinoid + Topical Abx
What would you give this patient for their acne?

Mild Closed Comedones
• Topical Retinoid
What would you give this patient for his acne?

Isoretinoin (oral)
Minimal scarring probably not the case for this guy:
• Retinoid + Topical antimicrobial+ oral Abx
What would you give this guy for his acne?

Mixed-Moderate Acne
• Oral Abx + Topical retinoid + topical Anti-microbial
Your patient wants to continue to use their OTC ance face wash after beginning treatment for thier acne. Can they?
This is NOT RECOMMENDED because it can lead to overdrying and irritation of the skin
What is the recommended basic skin care for acne?

T or F: Acne is caused by poor hygiene or dirt
FALSE, but a high glycemic index diet and MILK may perpetuate acne
Who is your typical patient that comes in with Rosacea?
• signs of rosacea?
A 1fair skinned 2women 3over 30 that has had 4**relapsing and remitting (chronic) bouts
Signs: Redness, Flushing, Pimples**
What are 4 causes of ROSACEA?
- Inflammation
- Demodex folliculorum - MITE that lives in the skin
- Vascular Abnormalities => people who tend to flush
- Genetic
What some Triggers of Rosacea?
- Sunlight
- Exercise
- Hot/Cold
- Stress
- Foods (spicy foods, hot coffee)
- EtOH
What are the 4 types of Rosacea?
• key features of each?
- Erythematotelangiectatic (more flat and rash-like)
- Papulopustular (looks like acne)
- Phymatous (Giant nose)
- Ocular (Red eyes)
What type of Rosacea is shown here?

Papulopustular - resemble acne
What type of Rosacea is shown here?

Phymatous - often manifests in the nose causing enlargment
What type of Rosacea is shown here?

Ocular - look how red the right eye is
What type of rosacea is shown here?

Erythromatotelangiectatic - rash-like
What are the Topical, Systemic, and invasive treatment options for these people?
Topical
• Metronidazole
• Azelaic Acid
• Sodium sulfacetamide with Sulfur
Systemic:
• Oral Tetracyclines
Other: IPL, Laser, Surgery
What is this?
• who is most commonly affected?

Perioral Dermatitis:
• Affects Women 20-45 years old
• Perpubertal Children
What are believed to be some of the causes of this condition?

Perioral Dermatitis Possible causes:
• Steroids
• OCP (oral contraceptive pills)
• Menstruation, pregnancy
• Fluorinate toothpaste
• Stress
• Candida, demodex mites
What are the key features of the condition shown here?

Perioral Dermatitis
Key Features:
• NOSE, EYES, and LABIA often affected
• Papules, pustules, vesicles
What is the treatment for Perioral Dermatitis?
#1 Discontinue ALL topical Steroids
Mild - topical abx
Severe - oral abx
NSAIDs can be used too
What are the 3 most common causes of Folliculitis?
• where is it typically found?
- Staph aureus
- Streptococcus
- Pseudomonas
Typically found in:
• Hair Bearing Areas (no shit)
What are some non-bacterial causes of folliculitis?
Fungal:
• Pityrosporum obiculare
Mites:
• Demodex folliculorum
Mechanical
Eosinophilic Folliculitis: HIV and Transplant pts.
What is this?

Folliculitis - notice that it typically occurs prominently in areas of friction
What is this?
• how would you treat it?

Folliculitis
Tx:
• Antibacterial soaps
• Topical antibiotics/antifungals
HIDRADENTITIS SUPPRUATIVA (HS)
•what is it?
• who does it occur in?
Recurrent painful abscesses of apocrine gland bearing areas like AXILLA, INGUINAL, INFRAMAMMARY FOLDS causing formation of sinus tracts leading to chronic damage. This is most common in women but can be in either sex (most often after puberty).
What risk factors are there for getting Hidradentitis Suppurativa?
Smoking
Obestity
Family Hx
How do you treat this disease?

Hidradentitis Suppurativa (HS)
Mild:
• Topical and/or Oral antibiotics
Moderate to Severe:
• Intralesional Steroids, TNF-alpha inhibitors, Surgery


