Academics Lesson VI—Customs Flashcards
Questions Influenced by Imperium by Julian Morgan and Liber Digitalis by David Jackson (32 cards)
What is the Latin term for “house”?
domus
Fun Fact: The Roman house (domus) in very early times consisted of one room, the ātrium. Over time the domus expanded to include several different rooms, some of which are common to us and some which are peculiar to the Romans.
What is the Latin term for the main room of a Roman domus, a room which originally was the only room of the house?
ātrium
Fun Fact: The Roman house (domus) in very early times consisted of one room, the ātrium. Over time the domus expanded to include several different rooms, some of which are common to us and some which are peculiar to the Romans.
In a Roman domus, which room is the kitchen?
culīna
Fun Fact: The Roman house (domus) in very early times consisted of one room, the ātrium. Over time the domus expanded to include several different rooms, some of which are common to us and some which are peculiar to the Romans. For instance, the Roman house included a kitchen (culīna), bedrooms (cubicula), and a dining room (trīclīnium).
In a Roman domus, which room is the bedroom?
cubiculum
Fun Fact: The Roman house (domus) in very early times consisted of one room, the ātrium. Over time the domus expanded to include several different rooms, some of which are common to us and some which are peculiar to the Romans. For instance, the Roman house included a kitchen (culīna), bedrooms (cubicula), and a dining room (trīclīnium). The Roman trīclīnium was slightly different from our dining room. In the trīclīnium were three couches (lectī). The Romans would eat while reclining on their left elbow on these lectī. In the center of the ātrium was a fountain, called the impluvium. The impluvium would receive rain water which fell through a hole in the ceiling called the compluvium. Attached to the ātrium were the alae (wings or alcoves) where Roman families kept their imāginēs (wax busts of the family’s ancestors). Each house had a tablīnum which served as the master’s study. The head of the house would keep important documents in the tablīnum in a chest called the arca. The Roman house also featured an open courtyard behind the tablīnum which contained a garden (hortus) with columns surrounding it called the peristylium. Other rooms in the house included a front door (ostium) and a backdoor (posticum), an entrance way from the street (vestibulum) and a foyer area or faucēs.
In a Roman domus, which room is the dining room?
trīclīnium
Fun Fact: The Roman house (domus) in very early times consisted of one room, the ātrium. Over time the domus expanded to include several different rooms, some of which are common to us and some which are peculiar to the Romans. For instance, the Roman house included a kitchen (culīna), bedrooms (cubicula), and a dining room (trīclīnium). The Roman trīclīnium was slightly different from our dining room. In the trīclīnium were three couches (lectī). The Romans would eat while reclining on their left elbow on these lectī.
In a Roman ātrium, what is the impluvium?
fountain / small pool which would receive rain water through a hole in the ceiling
Fun Fact: In the center of the ātrium was a fountain, called the impluvium. The impluvium would receive rain water which fell through a hole in the ceiling called the compluvium.
In a Roman ātrium, what is the co**mpluvium?
a hole in the ceiling where water falls into the i**mpluvium
Fun Fact: In the center of the ātrium was a fountain, called the impluvium. The impluvium would receive rain water which fell through a hole in the ceiling called the compluvium.
In a Roman domus, what are the wings that stemmed off the ātrium?
alae
Fun Fact: In the center of the ātrium was a fountain, called the impluvium. The impluvium would receive rain water which fell through a hole in the ceiling called the compluvium. Attached to the ātrium were the alae (wings or alcoves) where Roman families kept their imāginēs (wax busts of the family’s ancestors).
Kept in the Roman alae, what are the imāginēs?
wax busts of the family ancestors
Fun Fact: In the center of the ātrium was a fountain, called the impluvium. The impluvium would receive rain water which fell through a hole in the ceiling called the compluvium. Attached to the ātrium were the alae (wings or alcoves) where Roman families kept their imāginēs (wax busts of the family’s ancestors).
In a Roman domus, which room is the master’s study?
tablīnium
Fun Fact: Each house had a tablīnum which served as the master’s study.
In a Roman tablīnium, what name is given to the chest where Romans would keep important documents?
arca
Fun Fact: Each house had a tablīnum which served as the master’s study. The head of the house would keep important documents in the tablīnum in a chest called the arca.
In a Roman domus, what is the name given to the garden?
hortus
Fun Fact: Each house had a tablīnum which served as the master’s study. The head of the house would keep important documents in the tablīnum in a chest called the arca. The Roman house also featured an open courtyard behind the tablīnum which contained a garden (hortus) with columns surrounding it called the peristylium.
In a Roman domus, what is the name given to the hortus that is surrounded by columns?
peristylium
Fun Fact: Each house had a tablīnum which served as the master’s study. The head of the house would keep important documents in the tablīnum in a chest called the arca. The Roman house also featured an open courtyard behind the tablīnum which contained a garden (hortus) with columns surrounding it called the peristylium.
In a Roman domus, what is the name given to the front door?
ostium
Fun Fact: Each house had a tablīnum which served as the master’s study. The head of the house would keep important documents in the tablīnum in a chest called the arca. The Roman house also featured an open courtyard behind the tablīnum which contained a garden (hortus) with columns surrounding it called the peristylium. Other rooms in the house included a front door (ostium) and a backdoor (posticum), an entrance way from the street (vestibulum) and a foyer area or faucēs.
In a Roman domus, what is the name given to the back door?
posticum
Fun Fact: Each house had a tablīnum which served as the master’s study. The head of the house would keep important documents in the tablīnum in a chest called the arca. The Roman house also featured an open courtyard behind the tablīnum which contained a garden (hortus) with columns surrounding it called the peristylium. Other rooms in the house included a front door (ostium) and a backdoor (posticum), an entrance way from the street (vestibulum) and a foyer area or faucēs.
In a Roman domus, what is the name given to the entryway from the street?
vestibulum
Fun Fact: Each house had a tablīnum which served as the master’s study. The head of the house would keep important documents in the tablīnum in a chest called the arca. The Roman house also featured an open courtyard behind the tablīnum which contained a garden (hortus) with columns surrounding it called the peristylium. Other rooms in the house included a front door (ostium) and a backdoor (posticum), an entrance way from the street (vestibulum) and a foyer area or faucēs.
In a Roman domus, what is the name given to the foyer areas in the house?
faucēs
Fun Fact: Each house had a tablīnum which served as the master’s study. The head of the house would keep important documents in the tablīnum in a chest called the arca. The Roman house also featured an open courtyard behind the tablīnum which contained a garden (hortus) with columns surrounding it called the peristylium. Other rooms in the house included a front door (ostium) and a backdoor (posticum), an entrance way from the street (vestibulum) and a foyer area or faucēs.
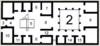
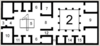
Identify the part of the house marked with the number 11.

cubiculum

Fun Fact: Here are all of the locations listed.
Identify the part of the house marked with the number 4.

faucēs

Fun Fact: Here are all of the locations listed.
Identify the part of the house marked with the number 15.
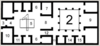
culīna

Fun Fact: Here are all of the locations listed.
Identify the part of the house marked with the number 3.

vestibulum

Fun Fact: Here are all of the locations listed.
Identify the part of the house marked with the number 8.

tablīnum

Fun Fact: Here are all of the locations listed.
Identify the part of the house marked with the number 10.

taberna

Fun Fact: Here are all of the locations listed.
Identify the part of the house marked with the number 6.

ala(e)

Fun Fact: Here are all of the locations listed.