A&P II Repro (Male) Flashcards
Produce gametes and secrete sex hormones
Gonads
Store and transport gametes
Ducts
Supporting Structures for Repro
Penis and Uterus
Branch of medicine concerned with male sexual dysfunctions
Andrology
Produce sperm and secrete hormones
Testes
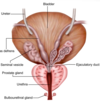
What are the ducts of the male repro system
- Epididymis
- Ductus Deferens (Vas Deferens)
- Ejaculatory Ducts
- Urethra
Accessory Sex Glands (Male)
(Provide Secretions to semen) - Seminal Vesicles - Prostate - Bulbourethal Glands
Supporting Structures (Male)
Scrotum Penis
Represents the fusion of the genital tubercles (embryonic development)
Raphe

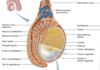
Layers of the Scrotum (Outer to Inner Layers)
- Dartos Muscle
- External Spermatic Fascia
- Cremaster Muscle (skeletal muscle/involuntary)
- Internal Spermatic Fascia
- Tunica Vaginalis (Parietal)
- Tunica Vaginalis (Visceral)

What separates Testes within the Scrotum?
Scrotal Septum

What are the two muscles involved in the cold/warmth reaction for the bean bag and the boys?
Cremaster: Contraction pulls the testes
Dartos: tightens the scrotum
Conditions that would inhibit the cremaster reflex
- Testicular Torsion
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Upper/Lower Neuron Dysfunction
- Cauda Equine Syndrome
Where do the testicles develop during fetal development?
Near the Kidneys and then drop through the inguinal canal in the 7th month
What is the inner most layer of the scrotum and the outer most layer of the testicle?
Tunica Vaginalis (Parietal / Visceral)

What anatomical feature causes you to be more predisposed to testicular torsion?
High riding Tunica Vaginalis, which prevents the Vas Deferens from attaching to the posterior wall of the scrotum

Which way does most testicular torsion rotate?
Medially, meaning that they must be massages laterally (Open book)
Layer of dense white fibrous tissue, a divide the testes into lobules
Tunica Albuginea

The functional unit of the testicles and what are the comprised of
Lobules, made of seminiferous tubules
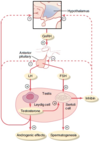
What are the two types of cells with in seminiferous tubules?
- Spermatogenic cells: Sperm Forming
- Sertoli (sustentacular): Support Sprematogenesis

What is Spermatogonia/spermatogenesis?
Primordial germ cells during fetal development that remain dormant until puberty

What are the functions of Sertoli cells (Nurse/Sustentacular)
- Maintains blood-testes barrier (Tight Junctions)
- Produce fluid for sperm transport INSIDE the tubules = righ in androgens, K+, and AAs
- Supports Mitosis and Meiosis (Stim by FSH/Testosterone)
- Support Spermiogenesis
- Secret inhibin (Neg feed back): Decrease GnRH/FSH production
- Produces ABP (Androgen Binding Protein/ Sex-hormone binding globulin): Increase local Testosterone
- Produce Antimullerian hormone in gestational growth (direct to boy rather than girl)

Cells that produce / secrete testosterone
Leydig Cells

What are the stages of spermatogensis?
- Spermatogonia/spermatogonium: Contains diploid (2n) number of chromosomes (46)
Under the influence of testosterone, these undergo mitosis - Primary Spermatocytes: Contains diploid (2n) number of chromosomes (46), Meiosis 1 begins at this point
- Secondary spermatocytes: haploid (n), contains 23 chromosomes, Meiosis 2 occurs at this point
- Spermiogenesis: Final stage of spermatogenesis