A First Look at the ECG Flashcards
(68 cards)
in what plane do standard limb leads look a events?
vertical (frontal)
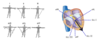
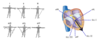
what are the 3 standard limb leads?
SLL I (left arm to right arm)
SLL II (left leg to right arm)
SLL III (left leg to left arm)

what are the basic principles of standard limb leads?
- fast events (depolarisation and repolarisation of action potential) are transmitted well
- slow events (plateau of the action potential) are not transmitted well
- a wave of approaching depolarisation causes an upward-going blip
what does each lead of the SLL record?
difference in potential between the two body parts
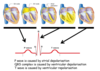
what can the depolarisation wave be compared to?
wave of water

what happens if a wave of depolarisation travels towards the left arm?
positive potential relative to the other node

what happens if a wave of depolarisation travels away from the left arm?
negative potential compared to other node

what happens if a wave of repolarisation travels towards the left arm?
Negative potential compared to other node

what happens if a wave of repolarisation travels away from left arm?
positive potential compared to other node
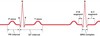
what does the P wave of an ECG represent?
atrial depolarisation
what does the QRS complex of an ECG represent?
ventricular depolarisation

what does the T wave of an ECG represent?
ventricular repolarisation

what does the flat line between the P wave and Q on an ECG represent?
plateau of atrial repolarisation

what does the flat line between S and the T wave on an ECG represent?
plateau after ventricular depolarisation

what does the plateau of atrial and ventricular repolarisation show a flat line on the ECG?
slow even so is not detected well

what is the PR interval?
time from atrial depolarisation to ventricular depolarisation
what is the time from atrial depolarisation and ventricular depolarisation called?
PR interval

what is the PR interval due to?
transmission through AV node
what is the time of the PR interval normally?
0.12 - 0.2s

what is the QRS interval?
time for the whole of the ventricle to depolarise
0.08s

what is the QT interval?
time spent while ventricles are depolarising
0.42s at 60bpm

what does the QT interval vary with?
heartrate

what cannot be seen on the ECG?
atrial repolarisation
coincides with ventricular depolarisation which involves much more tissue depolarising faster so swamps any signal
why is the QRS complex so complicated?
different parts of the ventricle depolarising at different times in different directions