8. Abdomen II Flashcards
What does the term intraperitoneal mean?
- organs are completely covered with visceral peritoneum
- organs are attached to each other or to the abdominal wall by a double fold of peritoneum
What is the abdominal cavity bounded by?
- Diaphragm
- Anterolateral abdominal wall – external and internal oblique, transversus abdominis and rectus abdominis and pyramidalis
- Posterior abdominal wall - vertebral column, quadratus lumborum, PSOAS major and iliacus
- Pelvic inlet
What is the pelvic inlet bounded by?
- Posterior : sacral promontory
- Arcuate line
- Pectineal line and pubic crest
- Pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint
What is everything below the pelvic inlet called and what structures are included?
- lesser pelvis
- (reproductive organs, terminal end of alimentary canal and bladder)
What 2 structures make up the abdominal cavity?
- greater pelvis and the abdomen proper
What is peritoneum?
- one continuous layer that is wrapped around all of the organs in the abdominal cavity
What is the difference between visceral and parietal peritoneum?
- Anything that touches an organ is known as visceral peritoneum and anything that is not touching an organ is called parietal peritoneum
What is peritoneal fluid made of?
- water, electrolytes,interstitial fluid, leukocytes and antibodies
Why is the peritoneal cavity open in females?
- space between the fimbriae and the ovary means that the peritoneal cavity in females is open
How does the peritoneum communicate with the exterior in females?
- via the vagina, uterus and uterine tubes in females
What does parietal peritoneum line?
- wall of the abdominal and pelvic cavities
What is the parietal peritoneum sensitive to?
- pain
- temperature
- touch
- pressure
What is the parietal peritoneum innervated by?
- T7-L1
What does the visceral peritoneum line?
- the abdominal and pelvic organs/viscera
What is the visceral peritoneum sensitive to?
- stretch
- tearing
What is the visceral peritoneum innervated by?
- afferent nerves that travel with autonomic supply to viscera it covers
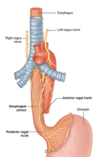
Label this image


What does over distension of the visceral peritoneum lead to?
- pain
Where is the peritoneal cavity?
- The space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum
What is contained within the peritoneal cavity?
- peritoneal fluid
What is the greater sac?
- space of the peritoneal cavity, posterior to the anterolateral abdominal wall
Why is pain from the abdominal region poorly localized?
- Dermatomes share a convergent spinal root with the autonomic nerve which supply that particular organ
What is the foregut region supplied by?
- greater splanchnic nerves
- T5-T9
What is the midgut supplied by?
- lesser splanchnic nerves
- T9-T11