1. Thorax I Flashcards
What is the significance of a Lump in the Upper Epigastric Region?
The Xiphoid Process has been Calcifed.
What are the True Ribs?
1st - 7th Ribs
Connect to Sternum via individual Costal Cartilages.
What are the False Ribs?
8th - 10th Ribs
Fuse together into a Common Costal Cartilage.
What are the Floating Ribs?
11th and 12th Ribs
How do ribs 11 - 12 differ from a typical rib?
Do not articulate with any bone anteriorly.
Which ribs are most commonly fractured?
7th - 10th Ribs
What is the significance of the lower rib’s proximity,
to the Abdominal Cavity?
They protect the organs in the Thoracic Cavity.
How many Vertebrae are in the Thorax?
12 Thoracic 12 (T12)
What is Thoracic Outlet Syndrome?
Group of disorders causing pain and paresthesis in the neck, shoulder, arms and hands.
Caused by compression of the Brachial Plexus and/or Subclavian Vessels,
As they pass through the Thoracic Outlet.
Anatomically the location is the Thoracic Inlet.
How are the Vessels at the Manubrium organised?
The Vein comes before the Artery.
The Vein is more Anterior.
The Artery is more Posterior.
What is the weakest part of each rib?
Just anterior to Angle of the Rib.
What structures are found at the Costal Groove?
V: Vein (Most Superior)
A: Artery
N: Nerve (Most Inferior)
What muscle attaches to the Scalene Tubercule?
Anterior Scalene Muscle:
- Attaches onto the Scalene Tubercle,
- On the inner border of the first Rib.
What does the Anterior Scalene Muscle divide?
Helps to divide the Brachial Plexus.
Also divides the Arterial and Venous supply of the First Rib.
List the arrangement of Structures over the First Rib:
From Anterior to Posterior:
- Subclavian Vein
- Anterior Scalene Muscle
- Subclavian Artery
- Brachial Plexus
What are all the Scalene Muscles?
- Anterior Scalene
- Middle Scalene
- Posterior Scalene
Where do the Scalene Muscles come from?
Come from the Transverse Processes of the Cervical Vertebrae.
Which are the atypical Ribs?
1st, 11th, 12th
What is a Cervical Rib and what are its consequences?
An elongation of the Transverse Process of one of the Cervical Vertebrae.
Impinges on the Brachial Plexus or the structure around it,
Leading to Paresthesia in the fingertips.
What is Costo - Chondritis?
Inflammation of the Cartilage that connects a Rib to the Sternum.
Why might damage to cartilage take a long time to heal?
It doesn’t have a very extensive vascular supply.
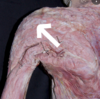
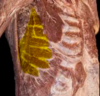
Pectoralis Major Origin:
Clavicular Part:
Anterior Surface of Medial Half of Clavicle.
Sternocostal Part:
- Anterior Surface of Sternum,
- Costal Cartilages of Ribs 1 - 6
Abdominal Part:
- Anterior Layer of Rectus Sheath
Pectoralis Major Insertion:
Greater Tubercle of Humerus
Pectoralis Major Action:
Shoulder Joint:
- Arm Adduction,
- Arm Internal Rotation,
- Arm Flexion (Clavicular Head),
- Arm Extension (Sternocostal Head);
Scapulothoracic Joint:
- Draws Scapula Anteroinferiorly