5 - Dougherty - Muscle Histology Flashcards
What are three basic types of muscle?
What do they all have in common/different?
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
Same contractile proteins, Different organization, Different regulation
Sarcolemma
Plasma membrane of muscle
Sarcoplasm
Cytoplasm of muscle
Sarcomere
Functional unit of contractile proteins (myofibril)
Repeating units run the length of the muscle fiber
Composed of thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments
Overlapping of filaments creates striation banding pattern
Skeletal Muscle Major Hallmarks
Single, long, multinucleated
flattened, peripheral nuclei
Cardiac Muscle Fiber
indeterminate number of cells joined end to end, 1 (maybe 2) rounded nuclei
Joined by intercalated disks
Smooth Muscle
Single cell, with single central nucleus
Hot dog nucleus (longitudinal, circular in cross section)
Eosinophilic cytoplasm, minimal endomysium
Skeletal Muscle Organization
[Fiber + Protective Covering]
Microfilaments (Actin/Myosin)
Myofibrils + Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Fibers + Endomysium
Fasicle + Perimysium
Muscle + Pimysium
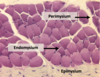
Three Connective Tissue Coverings in Muscle
Loose, Smallest: Endomysium
Dense:
Perimysium (middle)
Epimysium (largest)

What are the thick and thin bands of the sarcomere?
Dark and Light?
Thick - myosin (more letters = thicker)
Thin - actin (less letters = thinner)
Dark = A bands
Light = I bands
What is the point of attachment for the thin filaments?
What defines the length of the sarcomere?
Z-line
Z-line to Z-line = sarcomere
I Band
Light band
Z line and thin filaments (actin)
Shortens during contraction
A Band
Dark band
Full length of the thick filaments (myosin)
Thin filaments overlap here
No change in size during contraction
Muscle Triad
2 segments of sarcoplasmic reticulum bisected by T-Tubule
Located at the A-I Junction


What type of cells?
Orientation L and R?

L = Cross Section
R = Longituduinal Section

Motor End Plates
Type of Muscle?

Cardiac
Peep them center nuclei, branching, and intercalated disks
Type of Muscle

Cardiac
Center nucleus, branching
What makes the diad in cardiac muscle?
T-tubules at Z lines with sarcoplasmic reticulum
What cellular structure is required for coordination and propagation of action potentials between cells?
Gap Junctions
What binds intermediate filaments of two muscle cells together?
What are the intermediate filaments?
Desmosomes
Desmin, Vimentin
Purkinje Fibers
Note purkinje fibers are lighter in color and sub-endothelial.






