3.3.3.1 Proteins - Enzymes and Digestion Flashcards
The 2 stages of digestion in humans are…
Physical breakdown by teeth or stomach churning
Chemical digestion by enzymes
What is the function of the pancreas?
Releases pancreatic juice onto food, as it exits the stomach, which contains proteases, lipases and carbohydrases.
Give some examples of proteases involved in digestion
Endopeptidase
Exopeptidate
Dipeptidase
What is the function of teeth?
To physically bread down food and increase its surface area
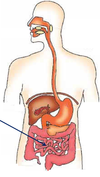
Identify the part of the digestive system

Oesophagus

Identify the part of the digestive system

Gall Bladder

What is meant by chemical digestion?
When large food molecules are hydrolysed into smaller molecules by enzymes.
Give some examples of carbohydrases involved in digestion
Salivary Amylase
Pancreatic Amylase
Maltase
Sucrase
Lactase
Name the cell membrane-bound protease
Dipeptidase
Bile salts are produced by the…
liver
What is the function of maltase?
To break down maltose into 2 α-glucose molecules
What is the function of the stomach?
Produces proteases for protein digestion
Churns food to physically break it down
Identify the part of the digestive system

Rectum

What is the function of salivary amylase?
To hydrolyse starch into maltose
What is the function of lipase?
To hydrolyse the ester bonds in triglycerides to give fatty acids and monoglycerides
How does the body break down maltose?
The lining of the ileum has maltase enzymes bound to their membranes.
Identify the part of the digestive system

Pancreas

What is the function of exopeptidases?
To hydrolyse the peptide bonds at the ends of peptide molecules, which releases amino acids and dipeptides.
Name the 3 membrane-bound disaccharidases…
Maltase
Sucrase
Lactase
What is the function of dipeptidases?
To hydrolyse the peptide bonds between dipeptides.
They are membrane bound enzymes.
What is the function of the ileum (small intestine)?
Produces enzymes to digest food
Absorbs the products of digestion into the blood.
What is the function of the oesophagus?
To carry food from the mouth to the stomach
What is the function of the large intestine?
To absorb water
Identify the part of the digestive system

Salivary Glands