#24 Virmani- Renal Disease Flashcards
RB has uncontrolled hypertension and an active UTI. Would you be able to get a renal biopsy?
NO. Contraindicated in:
Uncontrolled HTN
Bleeding disorders
Active UTI
Single Kidney (except transplanted kidneys)
What is the main clinical association?

Main clinical association
Glomerular disease (90%)
(picture of dysmorphic RBCs)
Labs come back with 3 RBC and RBC casts in the urine. What does this suggest?
Microscopic hematuria with renal origin.
Identify. Indicative of ?

WBC in urine
Pyuria
Identify
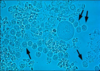
Sheets of WBC in urine
Suggestive of Pyelonephritis
Identify

Uric Acid Crystals
Flat with irregular shapes
Hyperuricosuria
Acute Uric Acid nephropathy
Gout
Identify

Calcium oxalate crystals
Ethylene glycol poisoning
Envelope = Ethylene
Hyperoxaluria
Identify

“Coffin Lid”
Alkaline urine with UTI
Triple Phosphate Crystals
Struvite stones
If you don’t like CATS (Coffin, Alkaline, Triple phospate, Struvite stones) you put them in a coffin.
Identify

Cystine crystals
Seen in cystinuria
likely congenital
Hexagonal shape
Identify

RBC Cast
Proliferative glomerular lesion
May be seen in acute interstitial nephritis
Identify

WBC cast
Interstitial nephritis
Pyelonephritis
Identify

Maltese cross
Lipid Bodies
Lipiduria
Your patient has a disproportionate increase in BUN. What are your differential diagnoses?
Volume depletion (prerenal azotemia)
GI bleed
Steroids or cytotoxic agents
High protein diet
Obstructive Uropathy
Hyper-catabolic States (infectin, fever, hyperthyroidism, cancer)
BUN/Cr ratio >10:1
BUN level is 18. Is this typically elevated, decreased or normal?
Normal
8-25 mg/dL
BUN varies inversely with GFR
Your patient has a disproportionate decrease in BUN. What are your differential diagnoses?
Low protein diet
Liver disease/cirrhosis
Overhydration (SIADH)
Malnourishment
BUN/Cr less than 10:1
Inulin is the ideal substance used to measure GFR because it is not reabsorbed, secrected, synthesized or metabolized. But since that is a pain, what endogenous substance is used and what formula is used?
Creatinine
CKD Epi
Breakdown of creatine phosphate
In differentiating pre-renal azotemia from renal tubular disease, what equation would you use?
FeNa
Una/Pna X Pcr/Ucr
or
(Una/Pna) / (Ucr/Pcr)
You are doing a macroscopic urinalysis and see green. What is that indicative of?
Red?
Yellow?
Turbidity?
Green - Urinary sedatives, triamterene, blue dyes
Red - blood, Hb, Mb, drugs (Phenitoin), dyes
Yellow - riboflavin, bilirubin (jaundice), pyridium, Rifampin
Turbidity - cells, casts, crystals
You have a patient that had a negative dipstick proteinuria but a positive protein/creatinine ratio. What might this suggest?
Benze-Jones proteinuria
Multiple Myeloma
You send a patient in for imaging because you want to distinguish if they have an obstruction or kidney atrophy. What kind of imaging will you order and why?
US
Non invasive, no contrast, painless
Can estimate kidney size, position and structural abnormalities
Detect obstruction, cysts, tumors
Locate best place for kidney biopsy
What imaging would you use for renal artery stenosis?
CT or MRI
(Virmani - MRI)
Why might you choose not to order an intravenous urography?
Does not work well on people with poorly functioning kidneys
Can cause contrast nephropathy


