#11 Katz - Imaging of the Kidney and Renal System Flashcards
List the three areas of constriction.
- Uteropelvic junction
- Pelvic inlet
- Uterovesical junction
You are working in a small rural office and US and CT are not available. You want to perform imaging of the kidney. What are you likely to order?
Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
You have ordered the IVP but what film should be done first and why?
Scout (flat) (KUB) abdomen so you can look for calculi. The contrast in the IVP would obscure the stones.
Which imaging would you order to look for calculi?
CT
In what situations would you not use contrast media in CT?
Allergies
Elevated BUN/Creatinine
Diabetic (If needed, keep well hydrated)
Identify

Phlebolith
Identify

Duplicated Collecting System
Identify

Horseshoe kidney
Corticomedullary differentiation
What are the advantages for using an ultrasound?
Non invasive
No radiation
Can detect hydronephrosis, renal masses & calcifications
Differentiating cysts from tumors
What type of resistance curve would be found on a Renal US in a patient with renal failure?

high resistance curve
What disease has been associated with the use of gadolinium-based MRI contrast in patients with severe renal disease?
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis

Identify

Right Renal Artery Stenosis
Identify

Right Renal Artery Stenosis
Your patient has fractured a transverse process in the lower thoracic area. What test should you order and why?
Urine analysis and imaging to check for ureter injury
Identify. What other image would you take?

Possible Renal Agenesis
Pelvic image to look for pelvic kidney

Identify

Pelvic Kidneys
Identify

Horseshoe Kidney
Calyces pointing in different directions
Abnormal orientation
Kidneys not along psoas shadow

When noticing dilated calyces, what could be a cause?

Duplicated ureters
Identify

Ectopic Ureterocele
What is the normal size of the kidney?
10-14 cm
Identify

Ureteral Reflux
What imaging has replaced IVU as the imaging modality of choice for detecion of urinary stones?
CT
Identify

Phlebolith with tail
CT
Identify

Renal Calculi near calyx
Low atherosclerosis of the aorta
Identify

IVP with partial obstruction
Patient presents with colicky flank pain with intermittent hematuria. What do you suspect?
Urinary stones
Identify

Staghorn Calculi
Struvite Stones
UTI
No contrast (obscured w/contrast)
Identify

Hydronephrosis
Calculi (seen on bottom image)
What treatment can be used to break up calculi over 5 mm?
Lithotripsy
ESWL (Extra Corporeal Shock Wave)
Kidney, Ureter or Bladder stones
What is the cell type of ureteral tumors?
transitional cell
Identify

Transitional Cell Carcinoma
(If it’s in the collecting system TCC)
Identify

Goblet deformity
Transitional Cell Carcinoma
Identify

Renal Pelvic Tumor
Would need to know there was contrast
Could use HU to differentiate (Calcium 1000)
Identify

Dilated Renal Pelvis - Newborn
Unilateral - UPJ obstruction
Medial uretal displacement might indicate?

Retroperitoneal mass
What is the most common renal mass?
Renal Cyst
What is a worrisome characteristic of a mass?
Calcification
87% with central and irregular calcification –> RCC
20% peripheral calcification –> RCC
ENHANCEMENT following contrast administration
You see the presence of fat in the kidney. What is the likely diagnosis? Benign or malignant?
Angiomyolipoma
Benign
On US, a renal cyst will show what characteristics?
Sharp interface between cyst and renal parenchymy
Round or Oval, anechoic (black)
Thin wall
Increased sound transmission
Identify

Renal Cyst
Identify

AD-PKD

A 53 year old patient presents with hematuria, flank pain and a palable mass. What do you suspect?
Renal Cell Carcinoma
What are the risk factors for renal cell carcinoma?
Modifiable:
Smoking
Obesity
Analgesics
NonModifiable:
Male
von Hippel-Lindau disease
Family History
Chronic dialysis
Identify

Renal Cell Carcinoma (Adenocarcinoma)
Not a cyst
Does not enhance like the normal kidney
Not uniform
Identify

Adenocarcinoma [RCC]
(Ultrasound)
Mass
Not cystic
3.5 year old presents with an abdominal mass. What do you suspect?
Wilm’s tumor
Identify
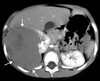
Wilm’s Tumor
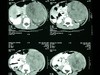
Renal Abscess is usually a complication of what gram negative infection?
E. Coli

Identify

Renal Laceration



