2 - Stroke Related Neuroanatomy-Neurophysiology Flashcards
What anatomical direction is this?

Axial
What anatomical direction is this?

Coronal
What anatomical direction is this?

Sagittal
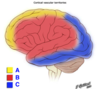
What anatomical direction are these?

A = Superior/Dorsal
B = Posterior/Caudal
C = Inferior/Ventral
D = Anterior/Rostral
Name the Layers of the Brain.

A = Scalp
B = Cranium
C = Dura Mater
D = Arachnoid
E = Subarchnoid Space
F = Pia Mater
G = Cerebral Cortex
Name the 4 Major Lobes of the Brain.
Frontal
Parietal
Temporal
Occipital
What Is “Controlled” By These Specific Areas Of The Brain?

A = Motor Control
B = Cognition, planning, + problem solving
C = Speech
D = Smell
E = Hearing
F = Facial recognition
What Is “Controlled” By These Specific Areas Of The Brain?

A = Touch + pressure
B = Taste
C = Body awareness
D = Language
E = Reading
F = Vision
G = Cerebellum
What are these neruo sulci?

A = Precentral
B = Superior frontal
C = Inferior Frontal
D = Lateral frontal (Sylvian Fissure)
E = Superior temporal
What are these neruo sulci?

A = Central (Rolandic)
B = Postcentral
C = Intraparietal
D = Lateral occipital
E = Lunate
F = Interior temporal
What is the homunculus?
An metaphorical representation of the way motor + sensory information is organized neurologically
What is the motor area of the brain called?
Precentral Gyrus
What is the sensory area of the brain?
Postcentral Gyrus
Which of Brodmann’s Areas are important to SLPs?
(4)
44 + 45 (Broca’s)
22 + 40 (Wernicke’s)
41 + 42 (Auditory Association)
39 (Angular Gyrus)
What happens when Brodmann’s Areas 44 + 45 are injured?
(2)
Broca’s Aphasia
Apraxia of Speech
What happens when Brodmann’s Areas 22 + 40 are injured?
Wernicke’s Aphasia
What happens when Brodmann’s Areas 41 + 42 are injured?
Processing issues in Wernicke’s Aphasia
What happens when Brodmann’s Area 39 is injured?
(2)
Acalculia
Agraphia
Label the following neruo landmarks.

A = Anterior cingulate cortex
B = Ventromedial prefrontal cortex
C = Orbitofrontal prefrontal cortex
D = Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
What is the ACC?
Anterior cingulate cortex
What does the ACC do?
(4)
Reward anticipation
Decision making
Empathy
Emotions
What happens when there is damage to the ACC?
(2)
Apathy
Poor motivation
What is the VMPC?
Ventromedial prefrontal cortex
What does the VMPC do?
Processing of risk + fear