2 Protein & Amino Acid Metabolism Flashcards
(60 cards)
Identify two major nitrogen containing compounds found in the body
- Amino acids (proteins)
- Purines + Pyrimidines (DNA / RNA)
Identify three minor nitrogen containing compounds found in the body
- Creatine
- Neurotransmitters e.g. dopamine
- Some hormones e.g. adrenaline
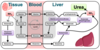
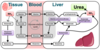
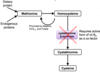
What is creatinine?
Creatinine is a breakdown product of creatine & creatine phosphate in muscle
What does measuring creatinine levels show us?
- -Indicator for renal function= raised is nephrons damaged
- Produced at constant rate and filtered via kidneys into urine
- Provides estimate of muscle mass:
- Creatinine urine excretion over 24h is directly proportional to muscle mass
- Provides estimate of muscle mass:
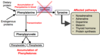
What is nitrogen balance?
Nitrogen balance is the measure of nitrogen input minus nitrogen output i.e. nitrogen input — nitrogen loss
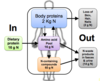
What is the clinical feature of a positive nitrogen balance?
In what instances in a positive nitrogen balance normal? (3)
- Intake > output
Clinical feature:
- Increase in total body protein
Normal state in:
- Growth, pregnancy or adult recovering from malnutrition
What is the clinical feature of a negative nitrogen balance?
In what instances in a negative nitrogen balance normal?
What may cause a negative nitrogen balance? (3)
- Intake < output
- Net loss of body protein
- Never normal (trauma, infection, malnutrition)
What is protein turnover?
Protein turnover is the balance between protein synthesis and protein degradation
Where do amino acids found in the body come from? (3)
- De novo amino acid synthesis
- Dietary protein
- Cellular protein
Provide an example of the following:
- Glucogenic amino acid
- Ketogenic amino acid
- Both ketogenic and glucogenic amino acid
- Glucogenic amino acid: alanine
- Ketogenic amino acid: leucine
- Both ketogenic and glucogenic amino acid: isoleucine
When are protein stores mobilised? (ie used for energy)
Occurs under extreme stress (starvation)
Describe the hormonal control over the mobilisation of protein reserves
Glucocorticoids stimulate the breakdown of protein to be used for energy

In de novo amino acid synthesis, where do the carbon atoms come from?
(Amino acids that can be synthesised de novo are Non-essential amino acids)
- Intermediates of glycolysis (C3)
- Pentose phosphate pathway (C4 & C5)
- Krebs cycle (C4 & C5)
In the de novo amino acid synthesis, where does the amino group come from?
Amino group provided by:
- other amino acids by the process of transamination
- (transfers an amino group to a ketoacid to form new amino acids)*
- from ammonia
Which compounds are synthesised from tyrosine?
- Catecholamines
- Melanin
- Thyroid hormones

Which compound is synthesised from histidine?
Histamine
Which compound is synthesised from arginine?
Nitric oxide
Which compound is synthesised from cysteine?
Glutathione
Hydrogen sulphide (signalling molecule)
Which compounds are synthesised from tryptophan?
- Serotonin (5HT)
- Melatonin
Which molecules are synthesised from glycine?
- Purines
- Glutathione
- Haem
- Creatine
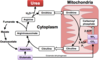
What has to happen to an amino acid to allow it to be used in oxidative metabolism?
- Removal of amine group
- carbon skeleton used
- Once removed nitrogen can be incorporated into other compounds or excreted from body as urea*
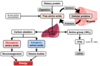
What are the two main pathways that facilitate removal of nitrogen from amino acids?
- Transamination
- Deamination
Explain the process of transamination

-
Aminotransferase enzymes
- use a-ketoglutarate
- funnel the amino group to glutamate
-
Aminotransferase enzymes
-
Exception to rule is Aspartate Aminotransferase
- uses oxaloacetate
- funnel amino group to aspartate
-
Exception to rule is Aspartate Aminotransferase

Which aminotransferase enzymes are measured routinely as part of liver function test?
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) which converts alanine to glutamate
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) which converts glutamate to aspartate