2 - MZH - Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells Flashcards
Difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
Eukaryotic = contains a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Prokaryotic = doesn’t have a true nucleus and doesn’t contain any membrane bound organelles
List all the eukaryotic organelles (14)
- Cell surface membrane/plasma membrane
- Cell wall
- Nucleus
- Chloroplast
- Mitochondria
- Endoplasmic reticulum (rough & smooth)
- Ribosomes
- Golgi apparatus
- Vesicles
- Lysosomes
- Microvilli
- Cytoskeleton
- Centrioles
- Undulipodia (flagella & cilia)
Define organelle + e.g?
A structure in a cell that has a particular function
E.g. Mitochondria produces ATP for cell respiration
Structure + function of:
Cell surface membrane/plasma membrane
S = Phospholipid bilayer and proteins of various types
F = Controls the entry and exit of materials

Structure + function of:
Cell wall
S = Ridgid structure found in plant cells, fungi cells and prokaryotic cells.
Plant (cellulose), prokaryotic (peptidoglycan), fungi (chitin).
F = Provide support. Porous to allow materials to pass through it. Channels called running through them called plasmodesmata enables transport between adjacent cells.
Structure + function of:
Nucleus (+ nucleolus and nulear pores)
S = Double membrane containing genetic material of cell. Contains nuclear pores on surface.
Nucleolus - dense body of DNA and RNA used to make rRNA for ribosomal units.
F = Holds onto and protect the genetic material from being damaged by the cytoplasm.
Nucleolus - controls: cell division, protein synthesis, production of mRNA for protein synthesis.
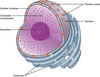
Structure + function of:
Chloroplast
S = Double membrane. Contains a fluid called stroma. Have internal networks called thylakoids (networks of membranes that form flattened sacs).
Several thylakoids = a granum (plural = grana)
F = Site of photosynthesis
Structure + function of:
Mitochondria
S = Spherical or sausage shaped. 2 membranes separated by a fluid-filled space. Inner membrane is highly folded to form cristae. Central part is called the matrix. Contains strands of DNA.
F = Produces ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Sites of aerobic respiration.

Structure + function of:
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
S = Series of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae. Continuous with outer nuclear membrane.
Studded with ribosomes.
F = Site of protein synthesis. Extensive in cells secreting proteins.

Structure + function of:
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
S = Series of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae. Continuous with outer nuclear membrane.
No ribosomes.
F = Site of lipid synthesis. Extensive in cells secreting lipids.

Structure + function of:
Golgi apparatus
S = Stack of membrane-bound flattened sacs “Cisternae”
F = Protein modification. Packages the proteins into vesicles so they can be transported, makes secretory vesicles, produce primary lysosomes.

Structure + function of:
Vesicles
S = Membrane-bound sacs found in cells.
F = Carry substances around the cell.
Structure + function of:
Ribosomes
S = Made in nucleolus of rRNA and protein. Eukaryotic ribosomes have 2 sub units.
Found: membrans of rough ER, cytoplasm, mitochondria and inside chloroplasts.
F = Site of protein synthesis (translation). Acts as an assembly line where coded info (mRNA) from nucleus is used to assemble proteins from amino acids.
Structure + function of:
Lysosomes
S = Spherical sacs surrounded by a single membrane
F = Contain digestive enzymes to break down material
e.g. old organelles, dead cells and ingested particles.
Structure + function of:
Microvilli
S = Approx 5µm long. Hairlike projections on the outer surface of cell.
F = Increase cell surface area
Structure + function of: Cytoskeleton
S = Intercellular proteins
Made up of 3 main components:
microfilaments
intermediate filaments
microtubules.
F = Microtubules are cylinder like and move microorganisms through a liquid or waft a liquid past a cell.
Aid transport within the cell.
Provides mechanical strength to cell.
Structure + function of:
Centriole
S = Animal cells only! Made of 9 triplets of microtubules arranged in a cylinder.
F = Help in the formation of the spindle fibres that separate the chromosomes during mitosis.

Structure + function of:
Undulipodia (Flagella & cilia)
S = Hair like structures that protrude from the surface of the cells. Each one is made of 9 microtubules arranged in a cylinder. Undulipodium are longer than cilia.
Looks like the flagella from bacteria but the have different internal structures.
F = To move cells e.g. sperm cells
What is the cell wall made of?
- Prokaryotic cells
- Eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic = Peptidoglycan
Eukaryotic = Cellulose
3 examples of prokaryotic cells
E.Coli
MRSA
Salmonella
Size of:
- Prokaryotic cells
- Eukaryotic cells
- Prokaryotic = 0.5-5µm
- Eukaryotic = up to 40µm
Difference between the ribosomes and DNA structure in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Reason?
Prokaryotic = 70s
Eukaryotic = 80s
Eukaryotic cell’s DNA are in linear form where as prokaryotic cells are not (they have one loop of chromosomes instead of 23 pairs of them)
Function of photosynthetic membranes and mesosomes?
Photosynthetic membranes:
-Increase SA for photosynthesis (prokaryotic cells)
Mesosomes:
- Folding of the plant membrane
- Increases SA for respiration
Another name for slime layer and its function (3)?
Capsule
Protects prokaryotic cell from:
- Drying up
- Hazardous chemicals
- Allows the cell to attach (sticky) e.g. Plaque bacteria


