2. Myology (Olinger) Flashcards
Identify the blacked out structures.


Which nerves innervate the anterior, middle, and posterior scalene muscles?
Anterior scalene: C4-C6.
Middle scalene: C3-C8.
Posterior scalene: C6-C8.
What innervates the anterior belly of the digastric muscle?
The nerve to the mylohyoid.
What are the infrahyoid muscles?
Sternothyroid muscle.
Thyrohyoid muscle.
Sternohyoid muscle.
Omohyoid muscle.
What is the innervation to the geniohyoid?
Fibers from C1, which travel with the hypoglossal nerve.
What is the innervation to the stylohyoid?
The facial nerve.
What is the innervation to the thyrohyoid muscle?
Fibers from C1 by the hypoglossal nerve.
What are the anterior borders for the superior, middle, and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles?
Where do they all attach posteriorly?
Anterior borders.
Superior – pterygomandibular raphae
Middle – hyoid
Inferior – thyroid cartilage
All three attach to the pharyngeal raphae posteriorly.
Identify the following blackedout structures.


Identify the blacked out infrahyoid muscles.


In which triangle is the thyroid gland contained?
Within the muscular triangle – a sub triangle of the anterior triangle of the neck
Label the following muscles.
In which triangle are they found?


What is congenital torticollis?
CN: Congenital Torticollis is a disorder produced by fibrous tissue tumor which forms in the Sternocleidomastoid M. which causes the head to turn and the face to look away from the affected side. A hematoma can arise and impinge on the Spinal Accessory N. which denervates the Stenocleidomastoid M.
What is the innervation to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle?
The facial nerve.
What are the two divisions for zones I, II, and III of the neck?
The angle of the mandible and the cricoid cartilage.
What innervates the sternocleidomastoid?
The spinal accessory nerve.
Identify the following posterior aspect laryngeal muscles.


What is the innervation for all of the laryngeal muscles except for the cricothyroid?
Recurrent laryngeal nerve.
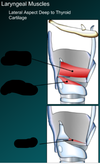
Identify the following muscles on the lateral aspect of the larynx, deep to the thyroid cartilage.

What innervates the anterior vertebral column muscles?
Anterior rami of the cervical spinal nerves.
Label the following three structures.


Where does longus capitis insert?
On the skull anterior to the foramen magnum.
Identify the following triangles and listed borders.


Identify the blacked out suprahyoid muscles.























