1. Osteology, Chondrology, Arthrology (Olinger) Flashcards
What are the three types of deep fascia of the neck?
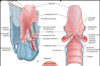
Investing layer of deep cervical fascia.
Pretracheal layer of deep cervical fascia.
Prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia.
Name the following ligaments the cricotracheal joint.


Infection between the investing layer of deep cervical fascia and the muscular part of the pretracheal layer of deep cervical fascia will typically exhibit what behavior?
The infection will typically be unable to spread past the manubrium.
Name the following thyroid cartilages.


Name the following ligaments of the cricothyroid joint.


What does the rima glottidis look like during normal respiration, forced respiration, phonation, and whispering?

Name the following bone markings.


Name the following ligaments of the epiglottic joint.

What kind of joint is the atlantoaxial joint?
Compound synovial.
What muscles can be involved in thoracic outlet syndrome?
Subclavius M.
Anterior, middle, and posterior scalene Ms.

What are the consequences of fractures of the laryngeal cartilages?
CN: Fractures of the Laryngeal Cartilages: Typically a result of a blow to the anterior neck in sports or compression by a seat belt in a motor vehicle accident. Results in a submucosal hemorrhage and edema, respiratory obstruction, hoarseness and in worst cases a temporary inability to speak.
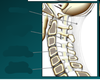
Which vertebra is this?
Identify the bone markings.


Name following structures of the fibroelastic laryngeal membrane.


Name the following bone markings.
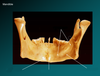

What ligaments do the anterior longitudinal ligament, posterior longitudinal ligament, and ligamentum flavum change into when they reach the occiput?
Anterior longitudinal ligament -> anterior atlantooccipital ligament.
Posterior longitudinal ligament -> tectorial membrane.
Ligamentum flavum -> posterior atlantooccipital ligament.
Name the following ligaments of the median atlantoaxial joint.

(Don’t forget the apical ligament of the dens attaching to the superficial margin of the alar ligaments beneath the superior longitudinal band.)

Name the following ligaments of the atlantooccipital joint.


Infection between the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia and the visceral part of the pretracheal layer of the deep cervical fascia will typically exhibit what behavior?
The infection in that area is likely to spread to the anterior thorax.
Name the following laryngeal cartilages.


Name the following cricoid cartilages.


Which of the laryngeal cartilages are elastic cartilage?
What are the rest made of?
The epiglottic cartilage is elastic.
The rest are hyaline.
What speck of cartilage can be found within the quadrangular ligament?
The cuneiform cartilage.
Name the following arytenoid cartilages.


Name the following pharyngeal ligaments.