1a.) Basic Topography Flashcards
(89 cards)
What components of nervous system are classed as:
- CNS
- PNs

Describe what grey matter is composed of
- Cell bodies and dendrites with rich blood supply
- There are axons in grey matter which allow it communicate with white matter, but volume predominatly cell bodies and dendrites
- Most of computation occurs in GM
Describe what white matter is composed of
- Myelinated and non-myelinated axons with no cell bodies
- Fibres (remember fibres are axons associated with suppporting cells- which is this case is Schwann cell)
- Myelin is white
- White matter pathways connect areas of grey matter
What is the PNS equivalent of:
- Grey matter
- White matter
- Grey matter: ganglion
- White matter: peripheral nerve
*NOTE: beware of term basal ganglia as this is actually grey matter in brain
How many spinal cord segments are there?
31 segments
Each segment has a pair of spinal nerves that go on to supply a given dermatome and myotome on each side

Describe where the grey and white matter are in the CNS
- Brain:
- Spinal cord: central core of grey matter, outer shell of white matter

If you have a sensory deficit in a homuncular pattern wherre may it suggest the lesion is?
Above thalamus
Define a funiculus (pleural: funiculi)
Segment of white matter containing multiple distinct tracts which both ascend and descend (hence often contain both sensory & motor)
State and describe the position of the three funiculi in spinal cord
- Dorsal funiculi
- Laterl funiculi
- Ventral funiculi

Define a tract
An anatomically and functionally defined white matter pathway connecting two distinct regions of grey matter. Impulses travel in one direction. Found within discrete places in the funiculi. All fibres in tract have similar function.

Define a fasciculus
A subdivision of a tract supplying a distinct region of the body
Cell bodies of grey matter in spinal cord is organised into cell columns; what name is given to these columns?
Rexed’s laminae (each column has a particular number)
If we think of all the lower motor neurones supplying a given muscle, these are found at multiple adjacent cord elvels (e.g. quads are supplied by L3, L4) and can be thought of as forming a distinct nucleus controlling that particular muscle
Define a nuclues and state whether it is white or gray matter
Collection of functionally relatd cell bodies
Grey matter
Define the cortex and state whether it is grey or white matter
A folded sheet of cell bodies found on surface of brain structure
Grey matter
How thick is the cortex typically?
1-5mm
Define a fibre and state whether it is grey or white matter
An axon in association withi its supporting cells (e.g. axon plus multiple Schwann cells)
White matter
The world ‘fibre’ is used synonymoulsy with what word?
Axon
State the three types of fibres and what each one connects
- Association fibres: connect cortical regions within the same hemisphere which are relatively to close to each other (NOTE: association fibrest that connect neighbouring gyri are called U fibres)
- Commisural fibres: connect left and right hemispheres or cord halves (an example is the corpus callosum)
- Projection fibres: connect cerebral hemisphere with the spinal cord/brainstem and vice versa

State what each of the following parts of brainstem are responsible for:
- Midbrain
- Pons
- Medulla
- Midbrain
- eye movements & reflex responses to sound and vision
- Pons
- Feeding
- Sleeping (particulary REM)
- Medulla
- Cardiovascular & respiratory centres
- Contains a major motor pathway (medullary pyramids)
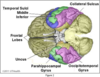
What sulcus separtes frontal and parietal lobes?
Central sulcus

Where is the primary motor cortex found?
Precentral gyrus

What does the lateral/Sylvian fissure separate?
Temporal lobe from frontal and parietal lobes
What does the parieto-occipital sulcus separate?
Parietal and occipital lobe