17. The Foregut Flashcards
Name the abdominal organ systems (4).
Gastrointestinal GI system
Biliary System
Pancreatic System
Renal (urinary) system
At what level does the esophagus enter the abdominen?
at T10
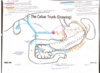
What are the 3 abdominal organ divisions?
- foregut
- midgut
- hindgut
Identify the various organs and the abdominal organ division they are found in.
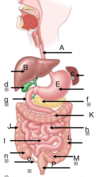
FOREGUT:
a. esophagus
b. liver (on right)
c. spleen
d. gallblader (holds bile) (under liver)
e. stomach
f. pancreas (tucked into duodenum)
g. 1/2 duodenum
MIDGUT:
starts at 1/2 of the duodenum (g)
h. jejunum
i. ileum
(DJ ILEUM)
o. appendix
n. cecum (1st part of the colon)
j. ascending colon
k. 1first 2/3 transverse colon
HINDGUT
starts at last third of transverse colon
L. descending colon
m. sigmoid colon
p. rectum
How are the abdominal organ divisions categorized?
divisions depend from where it gets its blood supply.
- the foregut receives blood supply from celiac trunk
- the midgut receives blood supply from superior mesenteric artery
- the hindgut receives blood supply from inferior mesenteric artery
artery branches from abdominal aorta

identify the 3 parts of the esophagus.

cervical part
thoracic part
abdominal part (very small): part after it enters diaphragm at t10

Identify the various parts of the esophagus.

A. superior esophageal sphincter (made by the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle)
B. longitudinal muscle (contracts up and down)
C. circular muscle (squeezes)
D. inferior espphageal sphincter (thickening of wall to stop acid reflux)
What parts of the esophagus aid in peristalsis?
the longitudinal and circular muscle
What prevents acid reflux?
the inferior esophageal sphincter aided by the diaphragm: when you breathe in, it contracts and flattens and closes off sphincter
Where is the stomach situated in the abdominen?
in the upper left quadrant at the transpyloric plane (L1)
Identify the various parts of the stomach. Where is the opening of the stomach found?
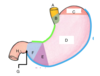
- the opening of the stomach is found at the end of the stomach
a. esophagus
b. cardia
c. fundus
d. body
e. pyloric antrum
f. pyloric canal
g. pyloric sphincter (pylorus)
h. duodenum - green line: lesser curvature of stomach
- blue line: greater line of stomach
What lines the inside of the stomach?
Rugae: folds that allow stomach to strech when food enters
=> if in lab you see smooth lining: stomach was full, if see rugae: stomach was empty

Where do the jejunum and ileum situate in the adominen?
jejunum: upper left quadrant
ileum: lower right quadrant
What are the three parts of the small intestine?
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
Identify the various parts of the duodenum. Identify wether the structure is retro or intreperitoneal.

A. D1: Superior part = intraperitoneal
B. D2: descending part : retroperitoneal
C. D3: inferior part: retroperitoneal
D. D4: ascending part :retroperitoneal and at end becomes intraperiotoneal because jejunum and ileum are intraperiotneal