17 - Molecular Diagnosis Flashcards
What are the ways of analysing DNA?
Nucleotide level - DNA Sequencing
Gene Level - Southern Hybridisation, Microarray, PCR variations
Chromosome level - Karyotyping, FISH
What are the ways of analysing proteins?
- Protein electrophoresis
- Immunoassays
- Fluorescent assays
What are restriction enzymes and why are they used?
- Produced by bacteria but we can use them
- Endonucleases
- Cut at restriction sites, usually forming pailindromes that are 4,5,6,8 b.p long
- Cuts can cause overhang and no palindrome
How would you figure out what DNA fragments will be formed when using restriction enzymes?
Different enzymes have different restriction sites and different genes have different restriction sites

How does DNA gel electrophoresis work?
- DNA negatively charged due to phosphate
- Place in electric field they will travel towards +ve electrode and separate in size
1. Gel
2. Buffer (conduct charge and not altter pH)
3. Power supply
4. Stain/Detection

How do you analyse a gel electrophoresis?
- Run a standard of known length DNA
- Can use ethidium bromide as a fluorescent tag as it is an intercalating agent

Why do we use restriction analysis?
- Investigate mutations (e.g CF)
- Investigate length of DNA fragments (deletions)
- Gene cloning
- Investigate DNA variation (fingerprinting)
How does gene cloning work?
- Isolate gene with restriction enzymes.
- Use same enzymes on plasmid vector
- Combine stick ends of plasmid and gene with DNA ligase
- Insert recombinant plasmid back into suitable host cell
- Identify and isolate the clone that contains the gene

Why do we use gene cloning?
1. Make useful proteins (specific insulin)
2. Find out what genes do
3. Genetic screening (Huntingtons)
4. Gene Therapy (aerosols with CF patients)
How is proinsulin produced by bacteria?

Describe the stages of the PCR?
- Heated to 95 degrees, causing hydrogen bonds to break and the strands to separate
- Cooled to 55 degrees to allow designed primers (forward and reverse) to anneal
- Heated to 72 degrees to allow TAQ polymerase (thermostable) to elongate DNA
- Exponential increase in DNA with each round of replication
THERMOCYCLERS
RESTRICTION ENZYMES

Why do we use PCR?
Amplify DNA fragment so can be coupled with restriction analysis (e.g fingerprinting)
What is the difference between protein and DNA electrophoresis?
- Different gel used
- Proteins can be separated on basis of charge
- Buffer used to maintain charge on protein
What technique is used to look at native proteins and what technique is used for non-native (nucleotide sequences) proteins?
Native: Gel electrophoresis
Non-native: SDS Page
What is serum protein electrophoresis?
- Proteins in serum ran on gel
- Laser shone through to measure how dark each segment is, shows how much protein present

What does this graph indicate?

- Not normal serum protein levels
- Monoclonal gammopathy, could be sign of myeloma
What is isoelectric focusing (IEF)

What is the SDS-page technique?
- Separation of proteins on the basis of their molecular weight not charge
- Gel electrophoresis but with denatured proteins
- 2 Mercaptoethanol and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate

What is 2D PAGE?
Mixture of IEF and SDS

How would you diagnose a disease with 2D page?
- Can compare a normal standard and see if a particular protein is being downregulated or over regulated by size

How do you identify a protein?
1. MASS SPECTROMETRY
2. IMMUNOASSAY

What are polyclonal and monoclonal anitibodies?
Poly - multiple antibodies to one antigen due to multiple epitopes
Mono - single antibody to specific antigen as one epitope (western blotting)

What is the western blotting technique?
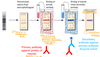
What is the ELISA test?
Can be used to measure amount of protein in blood, e.g insulin and cortisol





