17 - Marine Weather Flashcards
Heating of the Earth
- Curved Earth = Sun rays hit Earth at all angles
- Uneven heating of the Earth causes differences in air density in a change in pressure
Winds and Currents
Air flows from areas of high pressure into areas of low pressure
Types of motion in the atmosphere
- Vertical (currents)
- Horizontal (wind)
- Factors that contribute to winds and currents
- Air pressure
- Temperature changes
- Coriolis force
Air masses & fronts
A large body of air with generally uniform temperature & humidity
Front
Boundary layer between two types of air masses
- Different characteristics
- Types of Fronts
- Warm
- Cold
- Stationary
- Occluded
Warm Front

- Slides over and pushes the cold air
- Brings lighter but longer lasting rain

Cold Front

- Moves faster
- Pushes the warm air up
- Shorter rainfall
- Brings heavy storms/rains

Stationary Front

- When a cold front meets a warm front and none has the strength to push the other
- No movement between the fronts
- Rain may fall for many days

Occluded Front

- When a cold front catches a warm front, and the warm air lifts off the ground
- Can be cold or warm occluded depending on the temp. of the cold front
- Has both cold and warm front characteristics
- Heavy rain on cold side
- Light rain on warm side

Fog
Forms when warm, moist air blows over a colder surface and is cooled below its dew point
- Advection Fog is the most common type of fog

What are the two kinds of pressure systems?
- High Pressure
- Low Pressure
Circulation is on the opposite direction of the Southern Hemisphere
- i.e. High Pressure goes CCW, Low Pressure goes CW
High Pressure System
- Surface winds blow clockwise around a high pressure & diverge
- Generally areas of dry descending air
- Good weather is associated

Low Pressure System
- Surface winds blow counterclockwise around a low pressure & converge
- Sudden decrease in pressure
- Sudden decrease in temperature
- Sudden change in wind direction
- Bad weather is associated

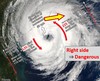
Hurricanes
Form when a low air pressure system develops over warm ocean waters with special wind patterns to propel them

Eye of the Hurricane characteristics
- Extremely low pressure
- Calm weather
- Surrounded by thunderstorm wall