15. Diarrhoea Flashcards
How is diarrhoea defined?
Roughly how much fluid is taken in/secreted endogenously in a day, and how much has to be reabsorbed in the gut?
What length of symptoms defines acute, persistent and chronic diarrhoea?
What would you ask about when taking a diarrhoea hx?
>200g stool/24h
Oral intake (**~2L**) + endogenous secretions (**~7L**) = 9L Intestine reabsorbs **~8.8L**
Acute: 2w (mostly infectious diarrhoea), Persistent: 4w, Chronic: >4w
Duration, organic features (wt loss, blood, nocturnal), systemic disease (thyrotoxicosis, DM), family hx (IBD, malignancy, coeliac), travel (infectious diarrhoea), medication (PPIs, NSAIDs, abx)
What infective causes are the following clues to:
a) Fever?
b) Rapid onset of symptoms after food (<6h)?
c) Bloody diarrhoea
d) Abx
What are the warning signs to look out for if a pt has diarrhoes?
What are some differential dx of diarrhoea?
a) Invasive bacteria (salm, shig, camp), enteric viruses, cytotoxic organism (C.diff, E.histolytica)
b) Toxin-producing organism (B. cereus, S. aureus)
c) Invasive bacteria (salm, shig, camp), amoebic dysentery (travel hx)
d) C. diff
Profuse watery diarrhoea + hypovolaemia, frequent bloody stools, temp >38.5oc, severe abdo pain, elderly/immunocompromised pt
Gasteroenteritis, infective colitis, diverticulitis (outpouching of colonic mucosa gets infected)
Describe E. coli. Which species are the most common cause of:
a) Traveller’s diarrhoea?
b) Infant diarrhoea in developing countries?
c) Contaminated meat?
d) Ulceration pattern and bloody diarrhoea?
What is haemolytic-uraemic syndrome?
Describe salmonella. What are the 2 types?
- *G-ve** bacilli, normal bowel flora.
a) Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
b) Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC)
c) Enterohaemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) - DO NOT give ABX for - can make it worse
d) Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
Disease characterised by triad of haemolytic anaemia, AKI and thrombocytopenia. Most cases preceeded by event of infectious +/- bloody diarrhoea acquired as a food-bourne illness or from contamined water by E.coli
G-ve, aerobic, flagellated. Typhoidal and non-typhoidal
Describe the course of typhoid.
Describe camphylobactor. What area does it primarily affect, and how is it contracted?
What is amoebic dysentry? What does it cause?
Week 1: fever, epistaxis
Week 2: fever, bradycardia, delirium, rose spots on abdomen and chest, diarrhoeal disease
Could also cause intestinal haemorrhage from Peyers patches, perforation in distal ileu, encephalitis, penumonia, thrombocytopenia. [Pic]
G-ve bacteria, S-shaped, 24-72h incubation, colon affected primarily, from raw chicken
Entamoeba histolytica, cysts (trophozoites) in water, soil, uncooked food. Trophozoites migrate to colon - bind to epithelial cells by producing lectin. Induce cellular necrosis and apoptosis. Ends up in liver -> ameobic liver abscess.

What is shigella? What does it cause, where does it mainly affect and how?
What is S.aureus? What does it cause and how?
What are the abx of choice for the following:
a) E.coli
b) Shigella
c) Vibrio cholera
d) Salmonella
e) Camphylobacter
f) Yersinia
G-ve anaerobic rod, causes bacterial dysentry, affects mainly colon. Produces enterotoxin Shiga + Verotoxin. Causes bloody diarrhoea
G+ve rod cocci, enterotoxins produced, rapid onset 1-6h, lasts <12h, vomiting + bloody diarrhoea
a) Ciprofloxacin (quinolone, most useful in gut infections if no sensitivities)
b) Quinolone/trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole (co-tramoxazole)
c) Tetracycline e.g. doxy/quinolone
d) Quinolone/co-tramoxazole
e) Erythromycin/quinolone
f) Tetracycline/co-tramoxazole/quinolone
What investigations would you do for diarrhoea?
How is acute diarrhoea treated?
Describe C.diff. What is the transmission route?
- *FBC** (U+E, LFT, ESR, CRP, TFTs, B12, folate, ferritin, vit D)
- Stool** (MC&S (microscopy, culture & sensitivity), CDT (C.diff toxin*))
- *AXR** - perforation?
- *+/- sigmoidoscopy**
- *WHO rehydration fluid:** 1L water, 3.5g NaCl, 2.9g trisodium citrate/2.5g sodium bicarbonate, 1.5g potassium sulphate, 20g glucose/40g sucrose
- And NO dairy or caffeine*
Gram +ve, anaerobic, spore forming, faecal-oral route, toxins A & B
List some risk factors of C. diff infection.
What symptoms would make you suspicious of C. diff?
What tests would you do to dx C. diff?
Abx (type, duration, multiplicity), increasing age (exclude infancy), severe underlying disease, NGT, anti-ulcer meds (PPI), ITU, long duration of hospital stay
Sudden onset watery diarrhoea, recent abx, disproportionately high CRP or WCC. Also fever, colic, low albumin and colitis. Don’t be distracted by underlying IBD
Request toxin A/B ELISA (30% in-pts asymptomatic colonisation, expensive, 25% false -ves), check stool CDT, MC&S in ALL pts with diarrhoea, flexible sigmoidoscopy (diagnostic in 50% non IBD pts) [Pic]

List some abx that commonly lead to C.diff.
How would you define mild, moderate, severe, complicated and life-threatening C.diff, and how would you treat it?
Cefuroxime, ciprofloxacin, meropenem, co-amoxiclav, tazocin, erythromycin
[Pic]

What are the arrows in the AXR showing?
How is this condition treated?
What is the tx for relapsing C. diff?
How is C. diff prevented?
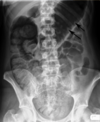
Poo in R colon - toxic dilation/megacolon
Medical tx: IV steroids. If no response - cyclosporine/infliximab
Surgery: CONSIDER IMMEDIATELY - mandatory if deterioration/tx failure. Decompression, and if fails then subtotal colectomy
Repeat metronidazole once only (overuse = irreversible neuropathy).
Tapered vancomycin, IV IgG, faecal enemas, pre-biotics (more preventative than tx, food for pro-biotics) and pro-biotics
Avoid unnecessary abx (and PPIs), hygiene for all - soap + water handwashing!, isolate and barrier nurse infected pts, vaccination against toxins A&B?


