1. Structure of DNA and RNA Flashcards
DNA is made from which monomer?
Mononucleotides (or just nucleotides)
Name the 3 components of a nucleotide
Phosphate group
Pentose sugar
Organic base (containing nitrogen)
In DNA, which base complements guanine?
cytosine
In RNA, which base complements adenine?
uracil
In DNA, which base complements thymine?
adenine
Idenitfy the 5’ and 3’ carbon atoms ofthe deoxyribose molecule.

Idenitfy the 5’ and 3’ carbon atoms ofthe deoxyribose molecule.

Identify the molecule.

Ribose

In RNA, which base complements guanine?
cytosine
In DNA, which base complements cytosine?
guanine
In RNA, which base complements uracil?
adenine
Which atoms will react to join the two nucleotides?

Which atoms will react to join the two nucleotides?
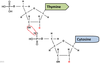
What shape does a molecule of DNA take?
A double helix
In DNA, which base complements adenine?
thymine
DNA is a stable molecule because…
- The phosphodiester backbone protects the chemically reactive base pairs.
- C-G base pairs contain 3 hydrogen bonds, so the more C-G base pairs in a DNA molecule the more stable it is.
- Interactive forces between base pairs add further stability (‘base stacking’)
How many hydrogen bonds are formed between Cytosine and Guanine in a DNA molecule?
3
Name the bond that forms between the 2 nucleotides of a dinucleotide.
Phosphodiester bond
What is the function of RNA?
To transfer genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes.
How is DNA adapted to carry out its function as a means of passing genetic information from generation to generation?
- Very stable - rarely mutates
- Hydrogen bonds between strands easy to separate for replication and protein synthesis.
- Very long - carries a lot of genetic information.
- Base pairs protected from chemical/physical forces by phosphodiester backbone.
Describe how are 2 DNA nucleotides form a dinucleotide
A condensation reaction occurs between the hydroxyl (OH) group on the 3’ carbon of Deoxyribose on 1 nucleotide and the hydroxyl group of the phosphate group on another nucleotide.
In RNA, which base complements cytosine?
guanine
How many hydrogen bonds are formed between Adenine and Thymine in a DNA molecule?
2
How are the 2 strands of DNA that make up the double helix held together?
Hydrogen bonds between complementary organic bases
What is the function of DNA
To carry genetic information
Name the 2 nucleic acids
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
Identify the molecule.

Phosphoric Acid
(phosphate)

Name the organic bases that can become part of a DNA nucleotide
Adenine
Thymine
Cytosine
Guanine
The phosphate group, pentose sugar and organic base of a DNA or RNA nucleotide are joined through which type of reaction?
Condensation reaction
The phosphate group attaches to which carbon atom of a ribose or deoxyribose molecule when forming a nucleotide?
The 5’ carbon atom (pronounced 5 prime)
Name the organic bases that can become part of a RNA nucleotide
Adenine
Uracil
Cytosine
Guanine
Identify the molecule.

Deoxyribose
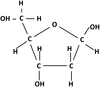
Describe how2 RNA nucleotides form a dinucleotide
A condensation reaction occurs between the hydroxyl (OH) group on the 3’ carbon of Ribose on 1 nucleotide and the hydroxyl group of the phosphate group on another nucleotide.
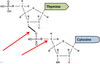
Which type of bond are the arrows pointing at?

Phosphodiester bond
If the bases on one strand of DNA are TGGAGACT, determine the base sequence on the other strand.
ACCTCTGA
If 19.9% of the base pairs in human DNA are guanine, calculate the percentage that is Thymine. Show your reasoning.
30.1%
If 19.9% is guanine -19.9% is cytosine as it is paired with it.
19.9 + 19.9 = 39.8%.
The remaining DNA is made from Adenine and Thymine, which is 60.2%. Thymine = 60.2% divided by 2 = 30.1%.
what is meant by degenerate when talking about the genetic code?
more than one triplet for each amino acid
What is meant by the term non overlapping when talking about the genetic code?
each base only read the once
How do the organic bases help to stabilise structure of DNA?
- Hydrogen bonds between the base pairs holds two strands together;
- Many hydrogen bonds provides strength;
Function of DNA helicase?
break H bonds between bases
Function of DNA polymerase?
join nucleotides together/reforrms phosphodiester backbone
Give 2 differences between the nucleotide in ATP (nucleotide derivative) and the nucleotides inDNA
- ATPhas 3 phosphates DNA 1 phosphate group per nucleotide
- ATP has ribose, DNA deoxyribose
- ATP - base always adenine, DNA it varies
Name the bone between the deoxyribose and the phosphate in a nucleotide
phosphodiester
Amount of hydrogen bonds between A and T
2
Polynucleotides
3 components join by condensation reactions to form nucleotidesNucleotides join to make polynucleotides with phosphodiester linksDNA stores the genetic code as a sequence of nitrogenous BASES
DNA key points
made of two antiparallel polynucleotide chainsBackbone chains are made from alternating sugar phosphate groups joined by a phosphodiester bond2 chains are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous basesbases contain nitrogen as well as carbon,hydrogen and oxygen
How is a polynucleotide suited to its function
Large molecule to store a lot of genetic information
How are polynucleotide chains held together by weak hydrogen bonds between bases
As each hydrogen bond is WEAK, polynucleotide chains can be easily separated. As there a LOT of hydrogen bonds collectively they STABILISE the HELIX.
How is a double helix adapted to its function
Genetic code of nitrogenous bases protected in the centre
How is the sugar phosphate backbone suited to its function
Adds stability to the double helix
How does the purine base always pairs with a pyrimidine base suited to its function
Means the 2 strands are parallel and allows DNA to be replicated and transfer information
RNA
also a polynucleotidesugar is ribosecontains the nitrogenous base uracil instead of thymineIt is a single polynucleotide chain and can fold back on itself if complementary bases form HYDROGEN bondsMuch SHORTER than DNA
mRNA
Carries instructions for polypeptide synthesis from nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm
tRNA
Carries amino acids to ribosome and matches them to the coded mRNA message
rRNA
Forms an important part of both subunits of the ribosome
Relationship between DNA, mRNA, ribosomes and tRNA
DNA - too large to leave nucleus. RNA carries GENETIC code to the RIBOSOMES in the CYTOPLASM and is used to help synthesise protein


Structure of DNA
The components of a DNA nucleotide are deoxyribose, a phosphate group and one of the organic bases adenine, cytosine, guanine or thymine.A DNA molecule is a double helix with two polynucleotide chains held together by hydrogen bonds between specific complementary base pairs.
Structure of DNA
The components of a DNA nucleotide are deoxyribose, a phosphate group and one of the organic bases adenine, cytosine, guanine or thymine.A DNA molecule is a double helix with two polynucleotide chains held together by hydrogen bonds between specific complementary base pairs.
Structure of RNA
- The components of an RNA nucleotide are ribose, a phosphate group and one of the organic bases adenine, cytosine, guanine or uracil.An RNA molecule is a relatively short polynucleotide chain.1 STRAND
Structure of tRNA
Transfer RNA has a cloverleaf shape. It is made from a single strand of RNA which folds due to base pairing to form this unusual shape. It has a triplet anti-codon site and an attachment site for a specific amino acid.
There are hydrogen bonds between some of the complementary bases
Structure of mRNA
- mRNA is a single-stranded molecule
- It is made up of a sugar-phosphate backbone and exposed unpaired bases
- Uracil bases are present instead of thymine bases (which are found in DNA)
Describe the structure of DNA
- Polymer of nucleotides;
- Each nucleotide formed from deoxyribose, a phosphate (group) and an organic/nitrogenous base;
- Phosphodiester bonds (between nucleotides);
- Double helix/2 strands held by hydrogen bonds;
- (Hydrogen bonds/paining) between adenine, thymine and cytosine, guanine


