1. Embryology Flashcards
How long is the “fetal/conceptional” age?
38 weeks (Gestation age: from LMP, 40w)
How long is the “gestational” age?
40 weeks
How long and what defines the “embryonic” period?
First 8 weeks
All major organs formed
How long and what defines the “fetal” period?
Remaining 30 weeks
Organs grow larger and increase in complexity
Define Zygote
The cell that forms when the ova and sperm fuse
What occurs during the first week after conception? (4)
- Zygote divides repeatedly
- Blastomeres = Daughter cells
- Morula (day 3)
- - - Entering uterus - Blastocyst (day 4)
- Inner cell mass
- Trophoblast

Define Morula
Solid cluster of 12-16 blastomeres at about 72 hours

When occurs on day 4 post conception?
Morula enters uterus and takes up fluid becoming a blastocyst

Types of Cells in the Blastocyst Stage (2)
Inner cell mass
Trophoblast
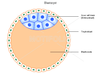
Define Inner Cell Mass
Forms the embryo
Define Trophoblast
Form the placenta
What occurs on day 8-9 post conception?
Implantation of the zygote

Three Primary Germ Layers (3)
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Mesoderm

The ectoderm and endoderm form what?
Sheets of epithelial tissue
The mesoderm forms what?
Mesenchyme tissue
Define Gastrulation
Invagination of epiblast cells

When does the endoderm form?
Days 14-15
(Mesoderm Day 16)
When does the mesoderm form?
Day 16

What occurs during days 16-18? (4)
- Epiblast cells invaginate (Gastrulation)
- Migrate anteriorly with endoderm cells
- Rod defining body axis formed
- Notochord is future site of vertebral column
What occurs during neurulation
Neural plate to neural groove to neural tube

What are the three regions of the mesoderm?
Somites: beginning of vertebral bones
Intermediate mesoderm
Lateral plate: forms cavity

When does the neural tube close?
Starts at the end of week 3 and completes at end of week form

What is the somatic mesoderm opposed to?
Ectoderm

What is the splanchnic mesoderm opposed to?
Endoderm









