09.18 Liver Flashcards
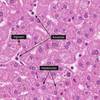
- Polygonal epithelial cell with one or more centrally located round nucleus with easily identifiable nucleoli
- Granular, eosinophilic cytoplasm with basophilic, perinuclear aggregates or rER.
- Arranged in one-cell-thick cords with sinusoid on either side

- Kupffer cells are actively phagocytic and represent the main cellular system for removal of particulate materials and microbes from the circulation (hepatic macrophage)

carry arterial/portal venous blood to terminal hepatic vein.
lined by specialized fenestrated endothelial cells which demarcate an extrasinusoidal space of Disse.
Kupffer cells project out on the luminal side

- The liver is covered by a capsule that branches and extends throughout the liver as septae
- The sheets of connective tissue divide the parenchyma of the liver into very small units called lobules

i. A potential space which contains loosely arrnaged extracellular matrix and several different cell tyeps important in host defense, nutrient metabolism and growth control of the liver

sinusoids with hepatocyte plates

how space of Disse creates lymph

Portal triad
- Located at the periphery of a lobule
- Bile duct, hepatic artery branch & portal vein branch
- Normally contains a few lymphocytes, macrophages and mast cells but NOT neutrophils of plasma cells

Portal triad
- Located at the periphery of a lobule
- Bile duct, hepatic artery branch & portal vein branch
- Normally contains a few lymphocytes, macrophages and mast cells but NOT neutrophils of plasma cells

lobule diagram.
portal triad on the left (bile duct, portal vein and artery)
central vein on the lower right.

each lobule has several portal triads on its periphery

- Hepatic acinus (of Rappaport)
i. Ellipsoidal mass of hepatocytes aligned around the hepatic arterioles and portal venules just as they anastomose into sinusoids

ii. Roughly divided into zones that correspond to distance from the arterial blood supply
a. Hepatocytes closest to the arterioles (zone 1) are the best oxygenated, while the farthest from the arterioles have the poorest supply of oxygen.

iii. Cells in the center of the acinus (zone 1) are the first the potentially absorb blood-borne toxins absorbed into portal blood from the small intestine.

hepatocytes, sinusoids, and portal triad

iii. Hepatocytes extract bile acids from sinusoidal blood and little escapes into systemic circulation
a. Bile acids are then transported across the hepatocytes to be resecreted into canaliculi

i. Emulsification of lipid aggregates
a. Bile acids have detergent action on dietary fat, which causes fat globules to be emulsified into fat droplets
b. Solubilization, and transport of lipids in an aqueous environment
• Bile acids are lipid carriers and are able to solubilize many lipids by forming micelles-aggregates of lipid that remain suspended in water

i. Intrahepatic bile ducts are lined by columnar epithelial cells
ii. Smaller, interlobular bile ducts are lined by cuboidal or low columnar epithelium

gallbladder wall has three layers
- Mucosa: branching folds lined by a single layer of columnar cells
- Muscularis
- Serosa: covered by peritoneum over the inferior aspect but is directly opposed to surface of liver on the superior aspect.
- No muscularis mucosae or submucosa (unlike the GI track)

gallbladder walls
simple columnar epithelium (glandular cells), lamina propria, fibroblasts, capillaires, from the top to bottom


