(09) Mastitis III Flashcards
(69)

(70)

(71)

(72)
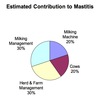
(73)
(Mastitis - Secret to Success)
(Two Simple Steps:)
1-2. what are they?
- prevent new infections
(herd level control,
problem = many contributing factors)
- eliminate existing infections
(individual cow management (treatment, dry-off, culling)
problem = detection, therapeutic failure)
(74)
5-point Mastitis Control Plane – what is it?

(75)
(1. Post-milking Teat disinfection)
1. goal = ?
2. teat dipping reduces number of new infections by how much?
3. disinfectants?
4. key to success = ?

(76)
- pre-milking teat disinfection for what?
- post-milking teat disinfection for what?

(77)
(2. Universal Dry Cow Therapy)
1. best chance of cure for what?
2. options?

(78)
(Universal Dry Cow Therapy)
(The Significance of Dry Period Infections)
- what % of all new infections caused by environmental pathogens occur during the dry period?
- Over what % of clinical coliform mastits events in the first 100 days in milk originated during the dry period?
1 50-60%
- over 50%

(79)
(Universal Dry Cow Therapy)
(Blanket Dry Cow Therapy)
- intramammary infusion with long-acting antibiotic at dry off
(purpose)
- cure what?
3 prvent what?
4.
- cure existing subclinical infections
- new infections that could be acquired during the dry period

(80)
(Universal Dry Cow Therapy)
(Blanket Dry Cow Therapy)

(80)
(Universal Dry Cow Therapy)
(Dry Cow Therapy)
(internal test sealant (orbeseal))
- administred when?
- May not be economically jus)fied in herds with a very low incidence of new infec)ons over the dry period
- Does work to help prevent new infec)ons
1 at dry off - after IMM Abx
(84)
(5. Regular milking machine maintencance)
(Milking Machine)
- vector for what?
- bacteria
(dirty equipment, contaminated milk “impacts”)

(86)
(5. Regular milking machine maintencance)
(Milking Machine)
- Determinant of what?
improper vacuum and pulsation setting and over-milking –> ?
- Hyperkeratosis (difficult to clean, disrupted barrier to bacteria?)
- teat end health
teat end hyperkeratosis
(87)
(5. Regular milking machine maintencance)
(Milking Machine)
















