(07) Mastitis I Flashcards
(2)
- successful repo –> lactation – ?
- what animals get mastitis?
- animals that nurse and wean - see increased inefction rate when?
- non-dairy animals - get primarily from what?
- mastitis
- all mammals
- just after parturition and weaning
- enivronment/hygiene (dairy animals can also get this way though)
(3)
- Why focus on dairy cows?
- mastitis = milk quality (animal health welfare, public health, economics)
- highest prevalence, economic, model
(4)
(Dairy Jargon)
- IMM =
- SCC =
- dry cows =
- fresh cow =
- transition period =
- DHIA =
- intramammary
- somatic cell count
- cows not milked for 30-60 days before calving to allow for udder regeneration and colostrogenesis
- recently calved
- +/- 3 weeks from calving
- Dairy Herd Improvement Association
(5)
- raw milk debate
- SCC limit is how many cells for grade A?
- bacteria limit is what?
- 750,000 cells/ml (no consquence of high SCC - just quality concern)
- 100,000 bac/ml (“standad plate count”)
(6)

(7)
(other quality/safety tests for antibiotics and other chemicals)
- all milk currently tested for what?
if found what is done with milk?
- B-lactam antibiotics
dumped
(testing for more becoming more common)
(8)

(9)

(10)
(What is mastits?)
- infection/inflammation of what?
- most due to what?
1 mammary gland
- bacterial infection (Very small % of cases are trauma/inflammatory with no infectious agent)
(11)
- what two ways do “bugs” get in?
- failure of what?
- through teat end, hematgenous (mycloplasma only)
2 host immunity (innate and adaptive (specific))
(12)
(Mammary Gland - innate immunity)
- Non-specific, present in mammary gland all the time, actvated quickly
- augmented by repeat exposure?
- physical barrier of the teat end, macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells, soluble factors
(13)
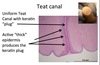
(Innate: Teat End)
- first line of defense, physical barrier
- Teat end contains sphincter muscle that does what?
- Teat canal line with what?
that does what?
- maintain closure between milking
- keratin
waxy, antimicrobial properties, physical barrier to migration
(14)
(15)
Innate: Cellular Defense
(somatic cells - SCC)
- normal population in mammary gland….
how many?
what predominates?
- During infection…
how many?
what predominates?
- <10^5 cells/mL
macrophages > neutrophils, lymphocytes, epi cells
- >10^6 cells/mL
neutrophils (> 90% of cells)
(Note… activity of these cells in the udder is impaired compared to activity in the blood due to milk environment)
(16)
(Innate: Cellular Defense)
- early is what?
- active is what?









