(09) Cranial Nerves Flashcards
(23 cards)
(Factors Responsible for Complex Internal Organization of BRain Stem)
There are five of them
also look at this
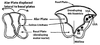
- The Fourth Ventricle (Medulla oblongata and pons are ventral to fourth ventricle, alar plate is displaced lateral to basal plate)
- Cranial nerve nuclei form discontinuous cell columns rather than continuous cell columns as seen in spinal cord
- Some cranial nerve nuclei migrate from their primitive embryonic positions (nuclei of nerves V and VII)
- Special senses (hearing, balance, taste, and vision) develop is association with the brain stem (SVA and SSA)
- Development of the cerebellum and its connections adds additional components
Know that sensory regions are displaced in brain stem

(Cranial Nerve Nuclei)
What is a nucleus?
Efferent nuclei are composed of cell bodies of what types of neurons?
Afferent nuclei consist of cell bodies of what type? What axons synapse on these and what is this connected to?
(Note distribution in picture)

- a profile of a column of neuron cell bodies
- of alpha and gamma motor neurons (SE) or preganglionic parasympathetic neurons (VE)
- of projection neurons and interneurons upon which primary afferent axons synapse in connection with ascending pathways or reflex activity
What do efferent nuclei do?
Afferent?
look at pic

- send axons out of the brain to innervate muscles or glands (3, 4, or 6)
- receive input from afferent axons entering the brain stem from cranial nerves
(MOTOR EFFERENT NUCLEI: basal plate derivatives)
(Somatic Efferent Nuclei)
- SE neurons form how many longitudinaly oriented but discontinuous columns of cell bodies in the brain stem?
- The neurons that comprise these columns are responsible for what?
- two
- innervating all of the skeletal musculature of the head
(MOTOR EFFERENT NUCLEI)
- Which nuclei are formed by a column of cells located near the dorsal midline of the brainstem?
- What do these nuclei innervate?
- What does damage to oculomotor (III), trochlear (IV), or abducent (VI) show up as?
- To hypoglossal (XII)?
- occulomotor, trochlear, abducent and hypoglossal nuclei
- muscles of the tongue and eye (derived from somites)
- abnormalties in eye movement, deviation of the eyes (strabismus)
- paralysis and atrophy of tongue muscles, deviation of tongue toward the side of damage, problems chewing and swallowing
- What nuclei are formed by a column of cells located in the ventrolateral brainstem?
- What did this location result from?
- These neurons innervate muscles derived from what?
- Motor nucleus of trigeminal N (V), Facial Nucleus (VII), Nucleus Ambiguus (IX and X)
- ventrolateral migration of the cell column during development
- somitomeres in pharyngeal arches
Damage to ….. presents as…..
- Motor nucleus of trigeminal n (V)
- Facial nucleus (VII)
- Nucleus Ambiguus (IX and X)
- paralysis of mastication muscles (bilateral = drooped jaw)
- Facial paralysis (innervates muscles of facial expression: ears, eyelids, nose and lips)
- swallowing and vocalization difficulties (innervates muscles of soft palate, larynx, pharynx)
- Which Nuclei represent the cranial portion of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (preganglionic parasympathetic neurons)?
- How many nuclei are recognized?
- How many do we need to remember?
- What are they?
- VE (Visceral Efferent) Nuclei
- 2
- 4
- parasympathetic nucleus of the vagus nerve and the parasympathetic nucleus of the oculomotor nerve
- What does the parasympathetic nucleus of the vagus (X) innervate?
- Damage to causes?
- What does the parasympathetic nucleus of oculomotor (III) innervate?
- Damage to causes?
- cervical, thoracic, and abdominal viscera
- accelerated heart rate, increased blood pressure, disturbances of gastrointestinal activity
- pupillary constrictor muscle and the ciliary body muscle of the eye
- loss of pupillary constriction in response to light in the eye on the side of the lesion
Damage to parasympathetic autonomic nuclei of the brainstem affects what?
- autonomic nervous system control of papillary constriction and cardiovascular function
Sensory Afferent nuclei are derivatives of what?
- alar plate derivatives
- What nuclei are represented by the sensory trigeminal complex which is located quite laterally in the brain stem?
- The complex is composed of three major subdiviions - what are they?
- GSA (General Somatic Afferent) Nuclei
- Nucleus of the spinal trigeminal tract (spinal trigeminal nucleus)
pontine nucleus of the trigeminal nerve (principal sensory nucleus)
mesencephalic nucleus of the trigeminal nerve
(Three major divisions of teh GSA Nuclei)
Nucleus of the spinal trigeminal tract (spinal trigeminal nucleus)
- Located where?
- associated with what stimulus?
- damage to causes?
- in the medulla
- pain and temperature sensation from the face and oral cavity
- loss of pain and temp sensation from half of the face
(Three major divisions of teh GSA Nuclei)
Pontine nucleus of the trigeminal nerve (principal sensory nucleus)
- location?
- associated with what stimulus?
- damage results in?
- pons
- touch and pressure sensation from face and oral cavity
- loss of touch and pressure sensation from face
(Three major divisions of teh GSA Nuclei)
Mesencephalic Nucleus of the trigeminal nerve
- Unipolar neurons located where?
- peripheral processes innervate what? and thus they what?
- Central processes innervate what? Function to do what?
- midbrain
- muscle spindles of masticory muscles; receive proprioceptive info
- motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve; function to help control the force of an animal’s bite
- What nucleus is located lateral to the GVE column?
- comprised of?
- GVA portion of this nucleus associated with?
- What does it do?
- GVA (General Visceral Afferent) Nucleus
- single nucleus termed the nucleus of the solitary tract (nucleus solitarius)
- cranial nerves IX and X
- It mediates visceral sensation from the pharynx, larynx, and portions of the esophagus
The nuclei of the special senses include what nuclei?
- SVA (special visceral afferent) nuclei
- SSA (special somatic afferent) nuclei
(SVA (Special Visceral Afferent) Nuclei)
Taste: There is a tast SVA complement in the nucleus of the solitary tract.
- Taste is associated with what cranial nerves?
- Damage will cause?
Smell:
- What nerve is associated with oldfactory SVA sensation?
- nerve found in brainstem? conducted to where?
- Damage will cause?
- VII, IX, and X (taste from tongue and pharynx)
- Loss of taste sensation
- olfactory nerve
- no; directly to piriform lobe of telencephalon
- will interrupt olfaction
SSA (Special Somatic Afferent) Nuclei
- These brain stem nuclei relate to what senses (and give corresponding nuclei)
Hearing:
- The medullary SSA column related to hearing and balance is located where? related to what?
Vision:
- The SSa nucleus related to vision is located where? associated with?
- Damage will cause (to II or VIII or their associated nuclei)?
- vision (lateral geniculate nucleus); hearing (cochlear nuclei); balance (vestibular nuclei)
- dorsally and laterally in brain stem; cranial nerve VIII
- in the thalamus; optic nerve/tract output
- profound on animal’s ability to see or hear
learn this - also check out diagrams if there is time

tongue will deviate to which side when damage
- deviates toward the side of damage
What is trigeminal neuropathy or neuritis?
drop jaw


