(01) Flashcards
(16 cards)
(Primary Funcition of CV system: Transport and Delivery)
1-2. Delivery of what two things?
- Removal of what?
- How must this occur?
- nutrients (O2, glucose, AA, fatty acids)
- other substanes (H2O, electorlytes, hormones, etc)
- wastes (CO2, lactic acid, nitrogenous wastes)
- at an adequate rate
(What is necessary to provide what the body’s tissues require?)
1-4. what four things?
- transport medium (blood)
- efficient transport system (vessels)
delivery (arteries), distribution (capillaries), return (veins)
- pump (heart)
energy to drive blood flow, perfusion pressure
- regulatory system (ANS, hormones, etc)
concept map - use if you wish - don’t memorize

(Transport in the CV system)
- bulk flow vs. diffusion
(bulk flow)
- what is it?
- what is needed to drive bulk flow?
- What is perfusion pressure? What generates this pressure?
- What is transmural pressure (aka distending pressure)?
- blood flow through vessels, rapid (seconds), travel long distances
- energy
- hydrostatic P from beginning to end of circuit; heart’s pumping activity
- pressure difference between inside and outside
(look at diagram)

(Transport in the CV System)
- What is the primary was dissolved substances move across vessel (capillary) walls from blood to interstitial fluid and vice versa? what is extracellular fluid outside of capillaries?
- What kind of process is diffusion? What is the driving force?
- What need to have close proximity to capillaries (fresh blood)? What three processes used to move substances?
- diffusion; interstitial fluid
- passive and relatively slow; concentration difference (from higher to lower)
- metabolically active cells; diffusion, facilitated diffusion, or active transport process
(Example: O2 tranposr –> both bulk flow and diffusion)
look at this - don’t memorize the numbers says she

(What is the path of blood flow?)
- where would blood flow take you?
cephalic vein - go over the order of blood flow… she says it around 20 minutes if you need to review this…

bulge in veins illustrates that veins can serve as storage area
- What is systole?
- what is diastole

- phase of ventricular contraction (blood ejected)
- phase of ventricuar relaxation (heart refills)
(arterial wall recoil –> propels blood)
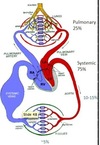
(Cardiovascular System)
- how many circulations linked in seires?
2-4. What are the three types of vesses and what are their functions?
- 2 (pulmonary and systemic)
- arteries –> high pressure conduit
- aterioles –> gatekeepers to capillaries
- veins –> return conduit
(there will be areas (or times) of low P and of high P)
for example - only high pressure in ventricles during systole
high pressure - arteries, ventricels (during systole),
low - veins, capillaries, atria (left and right), ventricles during diastole
(CV System)
(Pulmonary Circulation)
1-2. functions?
(Systemic Circulation)
- components?
2-3. functions?
- O2 and CO2 exchange
- acid/base regulation
- left ventricle, aorta, arteries to all systemic organs, capillaries, veins, atrium
- supply nutrients
- waste products
(note the parallel circuits in systemic)
(note there are also series circulations - two capillary beds in series) one is splachinch –> portal vein –> liver
also kidneys
- what is green?
- in orange?
- the blue?

- greater fluid pressure on lower valve (resistance of flow is same - but pressure is higher down low so flow increass)
- greater resistance to flow in left valve - therefore less flow in left - equal pressure on both
- because there is a pump there is equal pressure on each of these - but there are different resistances and therefore ifferent amounts of flow
(these illustrate basic principles of hemodynamics)
(Important Variables)
(Blood flow (f or Q)
CO distribution is also important - vasodilation or vasoconstriction…
learn this well

(Important Variables)
(blood pressure)
- another name for this?
- how is it measured?
- unit?
(pefusion pressure)
- what is it?
- how calculated?
(other)
(O2 tension, pH)
- transmural (distending pressure) P
- force/unit area of vessel wall (inside - outside P)
- mmHG, cm H2O
- force pushing blood through vessel
- mean P at the beginning - mean P at end (change in P)

(What is needed to maintain blood flow to maintain blood flow to the various regional circulations?)
1-3. what three things?
4-6. What are three things that can affect resistance?
- adequate arterial pressure
- adequate CO
- changes in resistance can influence both
- ANS - vasoconstriction
- hormonal mechanisms
- local regulation
know this really well she says

(Hemodynamic Principles)
- When referring to flow out of the heart (from either ventricle) (aka CO)…
- Q = ?
- CO = ?
- What is Systemic change in P?
- What is pulmonary change in P?
- does cardiac output from left ventricle equal cariac output from the right ventricle?
- 70-80% of systemic blood is in what?
- cardiac output
- change in P/R
- p1 = aorta, p2 = vena cava or right atrium (pressure in almost the same in both)
- p1 = pulmonary artery, p2 = left atrium
- yes
- veins (=storage reservoir)
(learn the percentrages in this picture)