Week 4: Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma/Liver & other PATH Flashcards
Compare and contrast DNA Polymerase Alpha vs. DNA Polymerase Delta
What is the helpful process that occurs after DNA Polymerase Delta activity?
DNA Polymerase Alpha: low fidelity copying, lacks proofreading, will be replaced
DNA Polymerase Delta: high fidelity DNA copying with proofreading function; reaches RNA primer, displaces it and inserts proper deoxyribonucleotides
MMR is the additional process after DNA Polymerase Delta activity, w/ almost no mutations
What are the components of the preinitiation complex?
General Transcription Factors
What are the functions of enhancers and silencers?
Enhancers enhance the effect of promoters, can fold in ways to end up near promoter and transcription initiation complex. Alone, they cannot effectively induce transcription but transcription factors can bind to them.
Silencers antagonize the effect of promoters. Repressors can bind to silencers.
What are Zn fingers?
DNA binding proteins that hold structure together by coordinating with cysteine side chains
What are dimerization domains? What results from their formation? Give an ex.
Proteins that recognize DNA can form homodimers or heterodimers via a dimerization domain to generate a hydrophobic effect
Ex: Leucine Zipper
What are the different types of transcription factors? How do they compare?
Activators (bind DNA)
Repressors (bind DNA)
Co-activators (↑ transcription rate but don’t bind DNA)
Co-repressors (don’t bind DNA)
General TF’s: part of Transcription Initiation Complex
What happens to RNA immediately after transcription? Why?
What is another event that occurs for a similar purpose? How is the site determined?
Capped w/ 7-methyl guanosine (m7G), required for export
Poly(A)-tail site determined by polyadenylation signal, also required for RNA export
What is alternative splicing and how is it modulated?
Is alternative splicing synonymous with mutation?
Physiological process of splicing RNA in different way bc of the presence of different set of splice activator and splice repressor proteins that bind to RNA
Alt splicing changes protein sequence through deletion/addition of residues or via a shift in codon reading frame
Alt splicing isn’t synonymous w/ mutation, even though mutation can generate a new splice site or alter a normally used one so that a cryptic splice site comes into use
What is the relationship between antibiotics and protein synthesis?
Give 3 classes of antibiotics (and ex’s) that can inhibit bacterial translation
Selectively inhibit protein synthesis by ribosomes in bacteria rather than human cells
Aminoglycosides: Gentamycin, Tobramycin, Amikacin
Chloramphenicol
Macrolides: Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Azithromycin
What are the 2 main components of Heme?
What are 2 things heme constitutes?
components: protoporphyrin and Fe2+/Fe3+
constituents: CytP450 Enzymes and Hemoglobin
Where is most heme made? Where is its secondary source?
Most heme is made in bone marrow, as part of hemoglobin synthesis
Less heme made in liver as cytochrome P450 synthesis
Describe the steps in Heme Synthesis: a) general
b) components
Synthesis from succinyl co-A and glycine w/ 3 consecutive condensation reactions that follow.
COOH groups trimmed & concludes w/ Fe insertion
(mit): glycine+succinyl COA-> ALA (->cytosol)
(cytosol) : ALA->
* *Porphobilinogen->
* *Hydroxymethylbilane->
* *Uroporphyrinogen III->
* *Coproporphyrinogen III->
(mit)
- *Protoporphyrin IX** -> +Fe2+
- Heme!*
How is Heme synthesis regulated by products from the liver and RBC’s?

Describe prophyrias in general terms
What are related lab findings?
Diseases of heme synthesis from enzyme deficiencies in synthesis pathway
PBG in urine/blood
Porphyrins in blood, urine and or feces;
ex: Coproporphyrin
Hydrophilic->Urine; ex’s: Uroporphyrin
Hydrophobic->(Bile)->Feces; ex: Protoporphyrin
Describe the pathogenesis of acute attack in AIP
with underlying genetics
PBG deaminase deficiency
AD Inheritance
Haploinsufficiency
Reduced penetrance

How can acute AIP present?
Rx?
ALA and PBG: neurotoxic
Seizures, respiratory failure possible
Abdominal pain (abdomen non-tender), anxiety, depression, psychosis
Tachycardia
Tx: ~400 g glucose/dose: hyperglycemia
What should AIP patients avoid?
Smoking
Alcohol: induce cyt P450
Drugs metabolized via Cyt P450: ex’s
diclofenac, chloramphenicol, erythromycin, lidocaine, barbiturates, sulfonamides, spironolactone, nifedipine, progesterone, progestins, sulfonylureas
Fasting/low carbohydrate intake (X Atkin’s Diet)
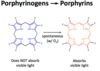
How can porphyrinogens become pathologic in Porphyria Cutanea Tarda?
Porphyrinogens can spontaneously form porphyrins
Porphyrins can then leak into blood and reach skin
Light can induce porphyrins to inflict oxidative damage
Describe the pathogenesis of PCT and other features
Deficiency of uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase
that can cause light-induced skin lesions
Liver porphyria (like AIP) but is NOT acute

Compare and contrast inherited vs. acquired PCT
Inherited (20%): AD, haploinsufficiency
*Decreased Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase activity in RBC’s
Acquired (80%): RF’s
Hepatitis C Virus
Smoking
Fe Overload (Hereditary Hemochromatosis)
Excessive alcohol intake (+ another RF)
*Normal Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase activity in RBC’s: damage only affecting liver
How do porphyrins in urine appear in PCT?
What are other lab findings in PCT?
Dark or fluorescent
↑ total porphyrins in urine
w/ more carboxylated porphyrins (esp uroporphyrin)
than coproporphyrin
mildly ↑ ALA and PBG
How is acquired PCT Tx?
Other recommendations?
Treat underlying cause
Phlebotomy for Fe overload
Avoid sun exposure
Beta-carotene: antioxidant effects and can reduce damage
Describe the enterohepatic circulation of bile salts?
Distal ileum absorbs primary and secondary bile salts via a Na-driven transporter (ASBT) and releases bile salts into blood so that they can move back to the liver and be re-secreted into bile
What are RF’s for cholesterol gallstones?
High bile concentration in gallbladder
Gallbladder empties at low rate
Bile system w/ low motility
Excess cholesterol secretion from fibrates: (gemfibrozil, fenofibrate) ↑ expression of cholesterol export proteins (PPAR alpha TF)
Decreased bile salt secretion from liver dysfunction or decreased bile salt reabsorption