Week 3: Osteology and Joints Flashcards
What are the two major parts of the skeletal system and what are their functions?
Axial – supports and proteccs organs of the head, neck and trunk
Appendicular skeleton – bones that anchor the appendages to the axial skeleton
What are the main components of the axial skeleton?
The skull, sternum, ribs and vertebral column
What are the main components of the appendicular skeleton?
The upper and lower extremeties, the shoulder and pelvic girdle
What is bone and what does it consist of?
Organ-calcified, living connective tissue made of:
Intercellular calcified matrix
Collagen fibers
Osteoblasts (build), osteoclasts (crush), osteocytes (mature)
What helps remodel bone?
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) (directs osteoclasts to break down bone when not enough Ca2+ is present)
Calcitonin (Ca2+-activated enzyme that “turns on” osteoblast activity)
Estrogen inhibits osteoclasts, which is why post-menopausal women can often get osteoporosis (activated osteoclasts break down bone)
What are the two major varieties of bone tissue and what are their relative amounts?
Compact bone – dense, outer shell that makes up 80% of the total bone weight, leads to greater strength and rigidity (but is very heavy) (ex.: humerus)
Spongy bone – less dense, lighter weight bone that makes up remaining 20% of bone, with spicules of bone enclosing cavities containing blood-forming cells (ex.: phalanges)
What are the major bones of the skull?
Cranium and mandible

What are the major bones of the upper extremity?
The humerus, radius and ulna

What are the major bones of the hand?
Carpals (wrist), metacarpals (palm) and phalanges (fingers)

What are the major bones of the thorax?
The sternum, ribs, clavicle and scapula

What are the major bones of the lower extremity?
The femur, patella, tibia (medial, larger) and fibula (lateral)

What are the major bones of the foot?
The tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges

What are the major bones of the pelvis?
The ileum, sacrum, pubis and ischium
What are the defining elements of long bone and where are they primarily found? What are some examples?
They are longer than they are wide, with a long shaft and two bulky ends, and are found primarily in the extremities. They are primarily compact bone in the diaphysis, with spongy bone at the epiphyseal ends. Examples include the humerus and femur.

What are the defining elements of short bones and where are they primarily found? What are some examples?
Short bone is cuboidal, with a thin outer layer of compact bone and mostly spongy bone in the center. The bones of the wrist and ankle are mostly short bones!
What are the defining elements of flat bones and where are they primarily found? What are some examples?
Flat bones are thin, flat sheets of compact bone plates separated by spongy bone. These include the bones of the skull and sternum.

What are the defining elements of irregular bones and where are they primarily found? What are some examples?
They are bones that are not either long, short, or flat. They are usually spongy bone covered in a small, compact sheath. These include the bones of the face, vertebral column and pelvis.
What are sesamoid bones?
They are round/oval-shaped bones found in an area where a tendon passes over a joint. These areas include the hand, knee, and foot (i.e. the patella). They act to protect the tendon and joint, and to increase their mechanical effect.
What is the periosteum?
A membrane that covers the bone and contains blood vessels, lymphatics and pain nerve endings. It is like a “placenta” for the bone that nourishes the bone and keeps it healthy. When you break a bone, nerve stimulation from the periosteum is what causes pain!
What is the main function of cartilage?
It supports soft tissues and provides a smooth, gliding surface for bone articulations at joints. It also enables development and growth of long bones.

How does the structure of cartilage change based on the amount of stress put on it?
In weightbearing areas, the amount of collagen in cartilage is greatly increased, and the cartilage is less flexible.
In areas of less stress, there are fewer collagen fibers and many more elastic fibers.
What is a joint?
A site where two skeletal elements come together (they don’t have to move)–elbows, teeth meeting the mandible, and ankles all represent joints
1) Skeletal elements separated by a cavity (synovial joint) tend to move
2) Skeletal elements held together by connective tissue tend NOT to move
What are the shock-absorptive elements of synovial joints?
Hyaline cartilage at the ends of bones acts as a shock absorber
Synovial membranes filled with synovial fluid act like a water balloon separating your fingers if you try to push them through–reduce friction and force on the bones
A fibrous joint capsule holds the synovial membrane and bones in place/together
What is the main component of synovial fluid?
Proteoglycans
What are the types of joints?
Plane
Hinge
Pivot
Condylar
Saddle
Ball and socket
What are the main movements of joints?
Uniaxial
Biaxial
Multi-axial
What occurs at a plane joint?
Sliding or gliding when one bone moves over the surface of another–not much movement can occur here
Ex.: tibiofibular, intertarsal, intercarpal, sternoclavicular
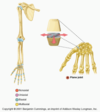
What occurs at a hinge joint?
Movement around one axis that passes transversely through the joint–permits flexion and extension, for example.
Ex.: Humeroulnar joint (elbow)

What occurs at a pivotal joint?
Allows movement around one axis that passes longitudinally along the shaft of the bone. It permits rotation.
Ex.: atlanto-axial joint of the upper cervival region, which allows us to turn our heads

What occurs at an ellipsoidal joint?
Allows movement around two axes that are at right angles to one another (like a mortar and pestle), permittingn flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction
Ex.: wrist, condyloid joint of fingers

What occurs at a saddle joint?
Saddle joints allow movement around two axes that are at right angles to each other, somewhat like an ellipsoidal joint. The articular surfaces are saddle-shaped (almost like kidneys), and permit flexion, extension, ab/adduction and circumduction.
Ex.: carpometacarpal joint of thumb, where thumb meets the hand

What occurs at a ball and socket joint?
Allows movement around mulitiple axes, permits flexion, extension, ab/adduction, circumduction and rotation. These joints are not well-protected and can be damaged easily.
Ex.: hip and shoulder joints

What are solid joints? What are some examples?
Solid joints are connections between skeletal elements where the adjacent surfaces are linked together by either fibrous connective tissue or by cartilage–movement is usually very restricted. These are called synarthroses.
Ex.: tibiofibular joint, radioulnar joint

What are sutures and where are they found?
Only found in the skull, involve adjacent bones linked by a thin layer of connective tissue.
What are gomphoses and where are they found?
They are the connection points between teeth and adjacent bones, where short collagen tissue fibers run between the rooth of the tooth and the bony socket. This has a “peg and socket” structure.
What are syndesmoses and where are they found?
Syndesmoses are where two adjacent bones are linked by a ligament, such as the radius and ulna. The ligamentum flavum connects adjacent vertebral laminae.
What are cartilagionous joints? What are the two kinds?
Cartilaginous joints are a kind of solid joint that connect skeletal elements by cartilage. Examples are intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis.
There are (1) synchondroses, which connect two ossification centers in one developing bone and (2) symphyses which connect two separate, fully ossified centers

What occurs at a synchondroses and what are some examples?
Synchondroses are primary carilaginous joints, which connect two ossification centers in the same developing bone.
Ex.: ribs, and the long bones of the humerus and femur

What occurs at symphyses and what are some examples?
Symphyses connect two separate but fully ossified bone centers, with cartilage between the two ossifies elements. These usually occur at the midline and include the intervertebral discs.



