Week 1: PNS Flashcards
(45 cards)
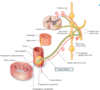
What is the basic schema of the PNS?
Input –> CNS –> Output
What is the term for the signal receptor nerves that come in from the body?
Sensory/afferent, which have both conscious (somatic) and unconscious (visceral)
Where do somatic afferent nerves send signals from?
Skin and skeletal muscles
Where do visceral afferent nerves sense signals from?
Internal organs
What is the term for output signals from the CNS?
Motor/efferent nerves, can be voluntary (somatic, skeletal muscles) and involuntary (visceral, ANS)
What does the somatic sensory system detect?
Temperature
Pain
Touch
Proprioception (position in space)
What does the visceral sensory system detect?
Change of internal environment of viscera, including stretch, temperature, pain, hunger, nausea, etc.
What does the visceral motor system act on? What is another term for this system? What are it’s main components?
The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) acts on smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands, and has sympathetic and parasympathetic components.
What are the two different types of nerves?
Spinal nerves (8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccyx)
and
Cranial nerves 1 - 12
Oh Oh Oh To Touch And Feel A Virgin Girl’s V Ah Bliss!
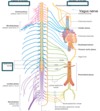
Identify A - J

A - somatic motor nerve
B - somatic sensory nerve
C - posterior root
D - spinal ganglion
E - spinal nerve
F - posterior ramus
G - anterior root
H - anterior ramus
I - anterior rootlets
J - posterior rootlets
The ventral/anterior root carries ____________ signals
motor/efferent (somatic and visceeral)
The dorsal/posterior root carries _____________ information
sensory/afferent (somatic and visceral)
The spinal nerve carries ____________ information
BOTH motor efferent AND sensory afferent (somatic and visceral)
The ventral/anterior ramus carries information to _____________
body walls and limbs
The dorsal/posterior ramus carries information to ____________
The deep back muscles and skin
What is the main difference between somatic and visceral motor outflow?
The somatic motor outflow is a single motor neuron connection between CNS and the target organ (skeletal muscle)
The visceral motor outflowm (ANS) is a two neuron connection (pre- and post-ganglionic) between the CNS and target organ (a gland, or cardiac/smooth muscle)
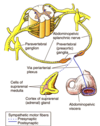
What are the two kinds of nerves of the ANS?
Preganglionic - originate in CNS and travel to ganglion to form a synapse
Postganglionic - originate in PNS and travel away from a ganglion at the point of a synapse
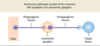
What are the principal differences between sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic and postganglionic nerves?
Sympathetic nerves have short pre- and long postganglionic fibers (T1 - L2)
Parasympathetic nerves have long pre and short postganglionic fibers (cranial nerves and S2 - S4)
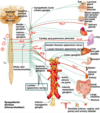
What are the activities that are involved with sympathetic activation of the ANS?
Heart rate and contractility increase
GI inhibition (decreased digestion/defecation)
Bronchodilation
Bladder muscle inhibition
Pupil dilation
Blood vessel tone increase (higher BP)
Genitalia (ejaculation)
Skin (sweating and piloerection)
What are the activities that are involved with parasympathetic activation of the ANS?
Heart rate decrease
GI movement, digestion, defecation
Bronchiolar constriction
Bladder contraction/urination
Pupil constriction for near vision
Genitalia (erection)
What actions do the para/sympathetic systems activate in regards to sexual activity? How do we remember this?
Erection = Parasympathetic = “Point”
Ejaculation = Sympathetic = “Shoot”
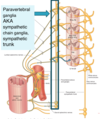
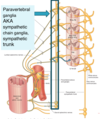
What pathway is “mandatory” in the sympathetic system? What pathway is “optional”?
All outgoing sympathetic signals exit through the ventral/efferent nerve, move through the spinal ganglia and spinal nerve, then circle “forwards” around to the white ramus communicans. All sympathetic preganglionic nerves must go through the white ramus.
However, not all postganglionic fibers behave the same–they have optional pathways. Some synapse at the ganglia there, and pass through the gray ramus communicans to the anterior or posterior perpiphery. Some pass through the ganglia and synapse elsewhere.
Why are there more gray rami communicans than white?
White rami communicans only exist in the T1 - L2 segment of the spine, where sympathetic nerves are connecting and passing through. There are many more “exit points” along the ENTIRE spinal cord, even outside of T1 - L2, where postganglionic sympathetic nerves are exiting to do their job.
How do sympathetic signals travel superiorly and inferiorly from a given thoracolumbar segment?
They pass through the ganglia of the sympathetic trunk, which extends farther than the thoracolumbar region of exiting sympathetic neurons.