Week 3 lectures (hearing and vision) Flashcards
(122 cards)
What the the stages of the process of perception
- sensory signal
- travels to sensory receptors
- Combine past experience and attention to create a
- Percept
- which leads to a perceptual understanding
- Which leads to a behavioural response
How does the amplitude of the sound wave affect the sound?
greater amplitude=larger sound
From what decibels can humans hear sounds?
0-140db
From what Hz can humans hear sounds?
20Hz to 20KHz
How does the frequency of the sounds wave influence the sound?
Higher frequency= higher pitch
Whats the outer ear consist of?
The stuff we can easily see and touch
the pinna/auricle
the external auditory canal
What is the tymphanic membrana also known as?
The eardrum

Which parts of the ear does the tymphanic membrane seperate?
The outer ear from the middle ear cavity

How many bones does the middle ear cavity have and what are they called?
malleus
incus
stapes

Where are the Auditory hair cells?
Cochlear

Where are the stapes?
In the middle ear, at the entrace to the cochlear

What to the stapes do?
The stapes are bones which move in a lever like direction to transmit information from the middle ear to the cochlear

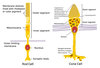
What two types of hair cells are in the cochlear?
The inner hair cells (main hair cells involved in detecting auditory stimuli)
the outer hair cells (plays a role in amplifying signals)
what two nerves in the ear come from the cochlear and combine to form one of the cranial nerves?
the cochlear nerve
the vestibular nerve

What are 4 functions of the outer ear?
Funnels sound inwards
amplifies the sound by acting as a tube for it to echo in
Shape of the pinna Helps sound localisation in the vertical plane
protection: earwax is water resistant, antibacterial and antifungal
the outer ear has an acidic environment
hairs in the outer ear prevent entry
What are two functions of the middle ear?
- protection- middle ear reflex can lock position of bones to prevent transmission of loud sounds
- Acoustic impedance matching- amplifies pressure created by sound wave to prevent loss of signal as it eners fluid filled cochlear
(when sound travels from air filled middle ear to fluid filled cochlear some sound waves are reflected back, meaning signal is lost. The shape of the middle ear increases the pressure created by the sound wave to prevent loss of signal)
what is 1?

pinna

what is 2?

malleus

what is 3?

The incus

What is 4?

The semicircular ducts

What is 5?

The vestibular nerve

What is 6?

The cochlear nerve

What is 7?

The cochlear

What is 8?

The auditory tube