Week 3 (From grey matter to white matter) Flashcards
What is a random neuron stain?
Golgi
(1 in 1000)
What are 3 selective stains?
Cell body stains
Myelin stains
Axon stains
What does the Nissel stain stain?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum of any cell
What does grey matter contain?
Cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons
What does white matter contain?
Myelinated axons
What 2 kinds of neuron does the spinal chord send signals to the body via?
Motor neurons
Autonomic preganglionic sympathetic neurons
What do autonomic preganglionic sympathetic neurons control?
Postganglionic neurons which then control glands and smooth muscle
From what neurons does the spinal chord recieve information about the body?
Sensory neurons
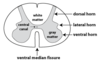
Where in the spinal chord cross section do motor neurons have their cell bodies?
Ventral horn (bottom)
Where in the spinal chord cross section do preganglionic neurons have their cell bodies?
Lateral horn (middle side bit)
What does it mean to say that sensory neurons are pseudounipolar?
It means that the cell body has moved so that the dendrite and the axon forms a single axon
Its called psuedounipolar because it starts off as bipolar
What kind of synapse connects an inhibitory neuron to a reflex arc
Axo-Axonic synapse
What is an axonal tracer?
A substance which can be carried along an axon in either direction
What is an anterograde tracer?
A tracer which is carried away from the cell body
What is a retrograde tracer?
A tracer which is carried towards the cell body
What does diffusion tensor imaging show?
The white matter tracts
Why can diffusion tensor imaging show the white matter tracts?
Water molecules are polarised
When they are constrained in very narrow structures such as myelinated axons the water molecules align along the axon tracts
Magnetic resonance signal at any given voxel has a vector
Vectors added together make fibres
What can diffusion tensor imaging not show about the white matter tracts?
The direction of axon travel
What information do the dorsal columns carry?
Information about touch and pressure

What information does the spinocerebrellar column carry?
Information about proprioception

What information does the spinothalamic column carry?
Information about pain and temperature

What information does the lateral column carry?
Movement information

Is white matter on the inside or the outside of the spinal chord?
on the outside

Is white matter on the inside or the outside of the brain?
On the inside