Lab 1 (Brain blood supply and nerve fibres) Flashcards
What is A?

The anterior cerebal
What is B?

The anterior communicating
What is C?

The internal Carotid
What is D?
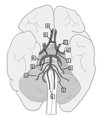
The middle cerebal
What is E?

The posterior cerebal
What is F?

The posterior communicating
What is G?

The Basilar
What is H?

The superior cerebellar
What is I?
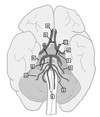
The anterior inferior cerebellar
What is J?

The posterior inferior cerebellar
What is K?

Vertebral
Where do the optic nerves meet and what is this called?
Where the optic nerves meet is called the optic chiasm.
The chiasm lies between the internal carotid arteries.
What does the oculomotor nerve do?
It controls some of the muscles that move the eye
It carries the connections that allow the iris to constrict
Where does the oculomotor nerve sit?
Between the posterior cebral and superior cerebellar arteries
What does the trigeminal nerve do?
Carries sensation from the face to the brain
Carries signals from the brain that control jaw muscles
Where is the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerve emerges from the lateral surface of the brainstem just below the superior cerebellar artery
What is the olfactory tract?
Ribbons of connections that extend forwards towards the underside of the cortex
What are the ridges of the brain called?
Gyri
What are the valleys of the brain called?
Sulci
What lobes are seperated by the central sulcus?
The frontal lobe (rostral) and the parietal lobe (caudal)
What lobe is outlined by the lateral fissure?
The temporal lobe
Where is the occipital lobe?
At the back of the cortex
Where are higher cognitive functions situated?
The pre frontal cortex
Where is vision situated?
The occipital cortex


