Week 19-20 - Peripheral Neuropathy & Spinal Cord Injury Flashcards
Epineurium
Surrounds entire nerve
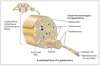
Perineurium
Encapsulates fascicle of nerves (bundles of axons)

Endoneurium
Contained within the perineurium and coating axons.

Blood-nerve barrier
between inner perineurium and endothelial cells of microvasculature within endoneurium
What are special senses?
Modalities that are carried by cranial nerves (i.e., olfaction, vision, tase, hearing/balance)
What are somatic senses?
Detected from all parts of the body (and head) and transmitted to the CNS via all spinal nerves except for C1 and the trigeminal nerve. Distinct from special senses, which are only carried by cranial nerves (i.e., vision, taste)>
Types of sensory receptors (4)
photoreceptors (rods and cones) thermoreceptors (central and peripheral) Nociceptors Mechanoreceptors (exteroreceptors and proprioceptors)
2 types of mechanoreceptors
Exteroreceptors respond to stimuli from outside the body (i.e., touch);
Proprioreceptors give information about position of the body, or its parts.
Generator potential vs action potential
Generator Potential is graded in amplitude (bigger stimulus has bigger GP) and does not cause the membrane to be refractory, nor does it actively propagate. Action potentials are all or nothing. They do cause membrane to bcm refractory to prevent backward propagation and they are actively propagated by regenerating themselves along the axonal membrane.
what is meant by the concept that the neuromuscular junction has a high safety factor
This refers to the fact that every alpha motor neuron AP will result in a muscle AP and subsequent contraction. Many parts of the physiology have developed to make this the reality (lots of VGNaCs etc).
Definition of anemia
A decrease in blood hemoglobin concentration. Can be the result of decreased RBCs or increased plasma. Normal ranges are age and sex dependent so the diagnosis of anemia differs based on these characteristics.
best marker for iron deficiency
Ferritin. Ferritin < 30 indicative or iron deficiency.
most common cause of iron deficiency anemia in the developed world is… What are the other causes of iron deficient anemia? (3)
Most common is occult blood loss! Bleeding Diet deficiency Malabsorption Increased need (children, pregnant)
What are the causes of microcytic anemias?
Acronym: TAILS Thalassemia trait Anemia of chronic disease Iron deficiency Lead poisoning Sideroblastic anemia
How are the generator potentials produced by mechanoreceptors, nociceptors, chemoreceptors, and photoreceptors different?
Mechanoreceptors produce a generator potential DIRECTLY in response to stretch (Na/K channels open in response to stretch). In contrast, nociceptors, photoreceptors, and chemoreceptors produce generator potentials INDIRECTLY via GPCRs.
The neuromuscular junction includes…
The presynaptic terminal of the alpha motor neuron, the synaptic cleft, and the post synaptic membrane of a muscle cell.
What is a motor unit?
1 alpha motor neuron and all of the muscle fibres that it innervates.
All of the muscle fibres innervated by a motor unit are the same type of fibres (fast, slow, twitch).
What is a motor unit pool?
All of the motor units that are involved in the innervation of a skeletal muscle.
Describe the basal lamina of peripheral nerves
it surrounds both the individual axon and myelin
Explain action potential propagation along a motor neuron (4)
An AP travels along an alpha motor neuron (MN) to all of its terminal branches.
- Ca2+ influx through voltage gated Ca channels stimulates release of ACh from vesicles at the distal end of the alpha MN
- ACh binds AChRs on shoulders of post junctional folds
- Na+ and K+ flow though AChR pore, which results in muscle membrane depolarisation
- this depolarisation is the ENDPLATE POTENTIAL
- AChE in the basal lamina hydrolyzes ACh to terminate NM transmission
Where is AChE located and its role
In the basal lamina/EC matrix of the synaptic cleft. Cleans up ACh swiftly so that contraction is v discrete.
What is the point of junctional folds on the post syanptic membrane
Large SA for AChR activation (located on the shoulders of folds)
What is the perijunctional zone
It is on the periphery of the site of muscle AP initiation. Has a high density of VGNaCs to ensure that muscle membrane reaches AP threshold (EPP is almost always large enough)
What is the point of T tubules on muscle cells?
They help bring AP deep into the cell.
They are continuous with the membrane. VGCa Channels on the t tubules pair with Ryanodine receptors on the SR to induce Ca release into the muscle cell.






