Week 1 Flashcards
What are the two differences between the right and the left kidney?
- Right and left differences
- Right kidney is lower than left due to the liver
- Right kidney is less protected by the ribs than the left because it is lower
Where do the ureters lie in relation to the transverse processes?
- Ureters run anterior to the lumbar transverse processes and sacrum
- Compare the sizes of the L and R renal artery and renal veins. Why are they different sizes?
- IVC is more right and aorta is more left
- Therefore, right renal vein is shorter than left renal vein; and right renal artery is longer than left renal artery
What two structures are the kidneys closest to? When is it important to be aware of this?
- Kidney are close to vital structures like the lung and liver – necessary to be aware of when trying to biopsy the kidney
What space are the kidneys, ureters, and the abdominal portion of the ureters in?
- The kidneys, ureters and the abdominal portion of the ureters are considered retroperitoneal organs. The retroperitoneum is extraperitoneal.
What are the two descriptors for organs in the abdominopelvic cavity (in terms of location?
What are the three spaces of the retroperitoneum called?
- The organs of the abdominopelvic cavity are described as being either intraperitoneal or extraperitoneal.
- The retroperitoneum is made up of three spaces, the perinephric (perirenal) space and the anterior and posterior paranephric (pararenal) space.
What are they yellow arrows pointing to?

- The kidney organ is surrounded by the perinephric fat which is surrounded by the perinephric fascia (yellow arrows) separating it from the paranephric space
Know these spaces.

Know them.
Label 1-4 (stages of contrast)

- Imaging – ability to access to physiology
- Non-Contrast (1)
- 0 seconds: normal, baseline
- Contrast enhanced
- Corticomedullary phase (2)
- 25-80 seconds: Cortex is enhanced
- Nephrographic phase (3)
- 80-150 seconds: enhances the cortex to medulla transition
- Pyelographic (excretory) phase (4)
- 3-15 minutes: hilum is enhanced
- Corticomedullary phase (2)
- Non-Contrast (1)
What is the route that urine takes in a nephron starting at the glomerulus?
- Glomerulus → Bowman’s capsule → Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) → Loop of Henle → Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) → Collecting Duct
What are the two parts of the nephrons and what parts of the nephron are part of each one?
- Two parts of nephron
- Renal corpuscle – filters blood plasma
- Glomerulus – capillary network
- Bowman’s capsule – surrounds glomerulus
- Located in the renal cortex
- Renal tubule – filtered fluid passes into
- PCT
- Descending and ascending loop of Henle
- Located in the renal medulla
- DCT
- Renal corpuscle – filters blood plasma

What are the types of cells in the following:
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Descending limb of loop of Henle
- Ascending limb of loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted & collecting ducts
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- simple cuboidal with brush border microvilli
- Descending limb of loop of Henle
- simple squamous
- Ascending limb of loop of Henle
- simple cuboidal to columnar
- forms juxtaglomerular apparatus where makes contact with afferent arteriole
- Macula densa
- Distal convoluted & collecting ducts
- simple cuboidal to columnar, principal & intercalated cells which have microvilli

What are the parts of the glomerular filtration barrier (inner to outermost)?
- Innermost to outermost
- Capillary endothelial cells –fenestrations covered by a thick glycocalyx (negative charge)
- Basement membrane
- Lamina rara interna – under the capillary endothelium; rich in polyanions
- Lamina densa – middle layer, contains collagen type IV, acts as physical barrier
- Lamina rara externa – supports podocytes - rich in polyanions
- Visceral epithelial cells (podocytes) – filtration slits covered by slit membranes, between interdigitating foot processes (pedicels)
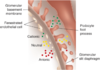
What is this showing?

Glomerular filtration barrier
What is the blood supply of the kidney from the renal artery to the renal vein?
- Renal artery → segmental artery → interlobar artery → arcuate artery → interlobular artery → afferent arterioles → glomerular capillaries → efferent arterioles → peritubular capillaries → interlobular veins → arcuate veins → interlobar veins → renal veins
What structure is shown and what does it contain (RC)?

Renal cortex containing renal corpuscles
What structure is shown on the lower half of this picture and what part of the nephron lies in this area?

Renal medulla and contains the loop of henle
What structure is shown on the lower half of this picture and what part of the nephron lies in this area?

Renal corpuscle made up of Bowman’s capsule and the glomerulus
Where vascular pole and between what two structures does it sit?

High density cells between the macula densa (MD) and the glomerulus
What is shown here and what kind of cells is it lined by?

Proximal convoluted tubule is lined with small cuboidal cells with microvilli brush border
What kind of cells is the DCT lined by?

Larger cuboidal cells without microvilli brush border
What is the arrow pointing too and where is this located?

- Macula densa
- Transition section between ascending loop of Henle and the DCT
- Located betwen afferent and efferent arterioles
What part of nephron is shown here and what two cells is it made up of?

- Collecting duct
- Made up of principle cells (light cells) and interacalated cells (dark cells)
What is the fuzzy blue stuff between each renal corpuscle? What is the darker blue stuff in the middle?

- Mesangial cells
- Fuzzy blue stuff between each renal corpuscle; dark blue areas are the nuclei












