Voiding Dysfunction Flashcards
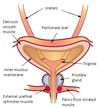
Understand LUT antatomy
There are three pathways of urine
What is the pontine micturition centers role in normal voiding
to coordinate contraction of the detrusor and relaxation of the sphincters; talks to PNS and SNS from lumbar and sacral area which innervates the bladder and the urethral spincter
Role of CNS in the micturition
– Voluntary control over micturition
– Inhibition of reflex detrusor contraction
Parasympathetic – facilitates micturition, how?
– Direct motor activation of detrusor contraction (acetylcholine; muscarinic receptors)
– Indirect facilitation of detruso rcontraction via stretch receptors
Sympathetic – facilitates urine storage
– Inhibition of detrusor
» Direct (β3- adrenergic receptors)
» Indirect (via inhibition of parasympathetic stimulation)
– Contraction of “internal sphincter”/bladder neck (α adrenergic receptors)
– Inhibition of detrusor
» Direct (β3- adrenergic receptors)
» Indirect (via inhibition of parasympathetic stimulation)
– Contraction of “internal sphincter”/bladder neck (α adrenergic receptors)
Sympathetic – facilitates urine storage
– Direct motor activation of detrusor contraction (acetylcholine; muscarinic receptors)
– Indirect facilitation of detrusor contraction via stretch receptors
Parasympathetic – facilitates micturition
Which part of the nervous system is under voluntary control?
Somatic – voluntary control
• Innervation of external urethral sphincter
responsible for smooth muscle sphincter contraction and relaxation
sympathetic nervous system; alpha-adrenergic fibers
Responsible for detrusor contraction and relaxation
cholinergic fibers; Parasympathetic Nervous System
Striated muscle sphincter contraction and relaxation
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic reflex between bladder and spinal cord promoting bladder emptying
Micturition Reflex
Bladder fills with urine causing stretching of bladder wall
Stretch receptors activated and send signals back to spinal cord that :
Further activation of stretch receptors with :
promote detrusor contraction
further promotion of detrusor contraction
CNS (cortex) sends inhibitory signals to __________micturition reflex in cognitively intact people (otherwise we’d peeing all the time like a baby)
“turn off”
Micturition reflex can also be abolished by
external sphincter contraction (guarding reflex, voluntary/involuntary contraction of sphincter)
When decision to urinate is made,______ removes the inhibitory signals and external sphincter relaxes to allow for micturition reflex to occur
CNS
Detrusor contraction via:
Internal sphincter relaxation via:
– Parasympathetic innervation
– Sympathetic innervation
have the potential to cause discoordination of these phenomena
• Damage to the brainstem/pons or spinal cord lesions below the brainstem
Detrusor contracts simultaneously with external sphincter (detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia)
Excessively high bladder pressures and trouble emptying bladder
What promotes urine emptying?
Release of central inhibition of detrusor (brain decides “it’s time to pee”)
External sphincter relaxes
Detrusor contracts
Bladder neck/internal sphincter relaxes
What promotes urine storage?
Descending signals from CNS inhibit detrusor
Detrusor at rest
Sphincters contracted
= Gas pedal of car
= Brakes
- Detrusor
- Urethral sphincters
________ = Car moving forward
________ ≈ detrusor contraction
________ ≈ relax urethral sphincters
• Voiding
– Foot on gas
– Take foot off brake
_______ = Car stopping/stopped
_________ ≈ detrusor relaxed
_________ ≈ sphincter muscles active
Urine storage
– Foot off accelerator
– Foot on brake
Failure to store urine
– Bladder (detrusor) – overactive (OAB) vs underactive
OAB/detrusor overactivity–>_________
Underactive detrusor with chronic urinary retention and bladder
overdistension–> _________
urge incontinence
overflow incontinence


