Visual System Flashcards
Visual System
Vision
- Very large area devoted to this sense in humans.
- Light passes through cornea > pupil > lens forms inverted & reversed image on the retina.
- Where the optic nerve enters the retina, no rods or cones, creates the optic disc which is the blind spot.
- Not superimposed so no functional blind spot.
Vision
- The fovea is the area of central fixation; region of highest visual acuity (highest amount of receptors).
- The macula surrounds the fovea, also high visual acuity.
Optic Field of View

Photoreceptors
- Rods.
- More numerous; 20:1.
- Do not detect colors & good for low light.
- Cones.
- Lots in the fovea.
- Can see color.
Receptive Field
- Receptive field of a neuron in visual pathway: portion of visual field where light causes excitation or inhibition on bipolar cells.
- Bipolar cells synapse onto ganglion cells that send axons into the optic nerve which exits through optic canal of sphenoid.
Optic Diagram

Optic Nerve, Chiasm, Tract
•Some fibers from the optic nerve cross over at the optic chiasm.

Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) & Extrageniculate Pathways
- Axons of retinal ganglion cells in optic tract synapse of the LGN of the thalamus.
- Continue to the primary visual cortex via optic radiations.
- Few fibers bypass LGN & enter brachium of superior colliculus (this is extrageniculate pathway).
- Relay to pretectal & superior colliculus go to Pulvinar > temporo-Parieto-occipital association love.
Figure 11.6 Geniculate and Extrageniculate Visual Pathways

Optic Radiations to Primary Visual Cortex
- Axons leave LGN (“C” shape around lateral ventricle) to go to primary visual cortex by Calcarine fissure.
- Called optic radiations.

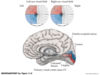
Primary Visual Cortex
- Upper portions à superior bank of calcarine fissure.
- Lower portions à inferior bank of calcarine fissure.
- Upper bank lesions:
- Contralateral inferior quadrant defects.
- Lower bank lesions:
- Contralateral superior quadrant defects.
- Fovea: 50% of visual cortex.
Left visual hemifields of the left and right eyes mapped to the primary visual cortex of the RIGHT hemisphere.
Visual Processing in Neocortex
- Most input arrives in layer 4.
- Thick layer due to functional importance.
- Subdivided into sub-laminae 4A, 4B, 4C α, and 4C β.
- Layer 4B has a lot of myelinated axon collaterals forming pale looking stria of Gennari can be seen in the gray matter with naked eyeball.
- Primary visual cortex (AREA 17) sometimes called striate cortex.
Primary Visual Cortex

Assessment of Visual Disturbances
- Detailed description of nature of visual disturbance.
- Such as time of course, if positive for phenomena (bright lights) or negative (regions of decreased vision.)
- Description of region of visual field defect of each eye involved.
Some Terms to Describe Visual Disturbances

Evaluation of Visual Disturbance
- Detailed history.
- Ophthalmoscopic exam.
- Visual acuity (Snellen chart).
- Visual fields.
Localization of Visual Field Defects
•Visual field testing
Visual Field Deficits
- Monocular scotoma.
- Monocular visual loss.
- Bitemporal hemianopia.
- Homonymous visual field defects? (retrochiasmal lesions.)
- Contralateral homonymous hemianopia.
- Macular sparing.
Figure 11.15 Effects of Lesions in the Primary Visual Pathways

VISUAL PATHWAY
https://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/vispath.html
Blood Supply & Ischemia In Visual Pathways
- Retina receives blood from branches of ophthalmic artery.
- Well visualized on ophthalmoscopic exam as emerge from optic disc.
- Emboli.
- Stenosis due to diabetes, HTN, or intracranial pressure.
- Vasculitis.
- Central artery occlusion or branch > infarct of all or part of retina.


