Neuroscience Major Plexuses and Peripheral Nerves Flashcards
(57 cards)
Brachial Plexus
- Nerve roots from C5, C6, C7, C8, T1.
- Major sensory & motor innervation for U.E.
- Robert Taylor Drinks Cold Beer.
- Roots, Trunks, Divisions, Cords, Branches.

Brachial Plexus
- Posterior cord – ARTS
- Axillary, Radial, Thoracodorsal, Subscapular.
- Musculocutaneous nerve – BBC
- Biceps, brachialis, coracobrachialis.

Figure 9.2 Brachial Plexus: Simplified Schematic
Lth = Bell’s long thoracic n.
DSc = dorsal scapular n.
SuSc = suprascapular n.
SuCl – n. to subclavius
LP = lateral pectoral n.
A = axillary n.
R = radial n.
T = thoracodorsal n.
S = subscapular n.
MP = medial pectoral n.
MC,A = medial cutaneous n. of arm
MC,F = medial cutaneous n. of forearm
Musc. = musculocutanous n.
Med. = median n.
Uln. = ulnar n.
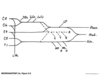
Figure 9.3 Lumbosacral Plexus

Figure 9.4 Lumbosacral Plexus: Simplified Schematic
Most Clinically Relevant:
F = femoral
Obt - obturator
Sc = sciatic
T = tibial
(CP = common peroneal)
SP = superficial peroneal
DP = deep peroneal

Lower Extremity Strength Testing:
https: //drive.google.com/file/d/0B5o1XviBdHwrOC1mNU5ZbEl0cFU/view?usp=sharing
https: //drive.google.com/file/d/0B5o1XviBdHwrc21rcHRBTlFEX00/view?usp=sharing
Important Nerves of the Leg

Important Nerves of Leg

Cervical Plexus
CN XII and C1 - C5
Phrenic nerve;
C3,4,5 keeps the diaphragm alive.
Brachial Plexus
- Axillary Nerve: C5, C6.
- Musculocutaneous Nerve: C5, C6, C7.
- Radial Nerve: C5, C6, C7, C8,T1.
- Median Nerve: C6, C7, C8, T1.
- Ulnar Nerve: C8, T1.
Five Important Nerves in the Arms

Five Important Nerves in the Arm

Upper Extremity Strength Testing:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B5o1XviBdHwrbU00cm9IaW9fMkE/view?usp=sharing
Thumb Strength Testing & Nerves:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B5o1XviBdHwrTGMxYWZNUlNnVGM/view?usp=sharing
Intrinsic Hand Muscles
innervated by ulnar nerve except LOAF
Lumbricals 1 and 2
Opponens pollicis
Abductor pollicis brevis
Flexor pollicis brevis
- Thunor eminence.
- Opponens pollicis, ABD pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis.
- Hypothenar eminence.
- Opponens digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi, ABD digit minimi.
- Lumbricals.
- Interossei.
Figure 9.6 Three Nerves Acting on the Thumb

Muscles Contributing to Flexion and Extension at Finger Joints

Upper Extremity Nerve Injuries
- Brachial plexus, upper trunk injury = (Erb-Duchenne palsy).
- Traction of infants shoulder.
- Motorcycle accident.
- Loss of C5C6 = weak biceps, deltoids, infraspinatus & wrist extensors.
Figure 9.7 “Bellman’s,” or “Waiter’s Tip,” Pose Assumed in Upper-Plexus Lesions

Upper Extremity Nerve Injuries
- Brachial plexus, lower trunk injury = Klumpke’s palsy.
- Grabbing a branch during a fall, TOS, Pancoast tumour.
- Weakness C8, T1 = hand & finger weakness, atrophy of hypothenar, sensory loos ulnar side of hand & forearm.
- If T1 is damaged proximal to sympathetic trunk; Horner’s syndrome: triad of miosis (constricted pupil), partial ptosis, and loss of hemifacial sweating (anhidrosis).
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Lower brachial plexus compressed between clavicle & 1st rib

*Cervical rib?
*ABD with ext. rot. increases symptoms & maybe decrease arterial pulse.
*EMG & X-Ray
Pancoast Syndrome
- Apical lung tumour (usually small cell carcinoma.)
- Affects lower brachial plexus.
- Sometimes Horner’s syndrome.
- Sometimes hoarseness (recurrent laryngeal nerve.)

Axillary Neuropathy
- Dislocation of proximal humerus compressing axillary nerve.
- Weak deltoid.
- Shoulder numbness.
- Differential dx – C5 radiculopathy.
(biceps).
Brachial Neuritis
- Unknown cause, inflammation?
- Burning shoulder or lateral neck pain.
- Weakness of muscles innervated by brachial plexus.
- Recovery usually 6-12 weeks.











