Viral skin infections Flashcards
(109 cards)
What causes both chicken pox and shingles ?
Varicella Zoster virus
Describe who are the usual affected individuals of chicken pox and what happens after the infection has subsided ?
- Typically occurs in children
- After subsiding the virus establishes latency in dorsal root ganglion
What are the main symptoms of chicken pox ?
- Fever initially then other symptoms develop
- Itch
- Systemic upset is usually mild
- Rash - goes from macules to papules to vesicles to scabs to recovery

How is chickenpox diagnosed ?
Clinically
What are some of the complications of chicken pox ?
- Secondary bacterial
- Pneumonitis
- Disseminated haemorrhagic chickenpox
- Scarring, absent or minor
- Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain, caused by infection or an allergic reaction)
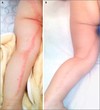
Pic below shows a haemorrhagic rash caused by chicken pox

What should not be given to patients with chickenpox and why?
NSAID’s - because it increases the risk of secondary bacterial infection
Appreciate this story of a man developing varicella penuomia
A 26-year-old man presented with a 5-day history of cough, fever, and mild dyspnoea. He had an exanthematous vesicular rash that had started 3 days before the respiratory symptoms began. He smoked cigarettes (30 per day for the previous 14 years). His daughter had recently had chickenpox; he had not been vaccinated against the disease nor did he have a history of it. A skin examination revealed a polymorphic rash with vesicles, pustules, and crusty lesions (Panel A). Chest radiography performed at the time of admission to our hospital showed multiple small nodules in both lungs (Panel B). There was no evidence of central nervous system or liver involvement. High-resolution computed tomography revealed numerous ill-defined nodules, 1 to 5 mm in diameter. Coalescence and surrounding halos of ground-glass attenuation were also observed in some nodules (Panel C). Serologic testing for the human immunodeficiency virus was negative. The diagnosis of varicella pneumonia was made on the basis of the rash, pulmonary symptoms, and contact with a child with chickenpox. The patient was treated with intravenous acyclovir. Follow-up chest radiography, performed 7 days after admission, showed that the nodules had disappeared. The patient had a full recovery.
What is neonatal varicella zoster virus ?
It is when the mother gets chickenpox dring pregnancy which can then be passed on to the baby associated with more sever complications

In who may chickenpox present more severe ?
- Very young (neonates) or very old patients
- Immunocompromised
What is the treatment of chickenpox in health individuals ?
- Paracetamol + calamine lotion for the itch
- Keep cool & trim nails
For immunocompromised patients & newborns with peripartum exposure to chickenpox (i.e. havent yet developed it themselves) what should be given?
Varicella zoster immunoglobulin (VZIG).
If an immunocompromised patient or neonate develops chickenpox what should be given to treat it ?
IV aciclovir
What is given to pregnant women if they have exposure to someone with shingles/chickenpox?
Varicella Zoster Immune Globulin
What should be given to pregnant women who are found to be seronegative for varicella-zoster virus immunoglobulin G (VZV IgG)
Varicella vaccination prepregnancy or postpartum
If a pregnant women develops chickenpox what treatment should be given ?
- PO aciclovir if they present within 24 hours of the onset of the rash and if they are 20+0 weeks of gestation or beyond.
- For severe chickenpox all pregnant women should recieve IV aciclovir
What is shingles (or herpes zoster) ?
- Shingles is an acute, unilateral, painful blistering rash caused by reactivation of the Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV).
- It is also known as herpes zoster

What are some of the features/symptoms of shingles ?
- There is usually a prodromal phase with abnormal skin sensations and pain in the affected dermatome e.g. burning, stabbing, throbbing for 2-3 days before rash appears
- Dermatomal distribution
- Tingling/neuralgic type pain to erythema, to vesicles, to crusts
How is shingles diagnosed ?
Clinically
Who is shingles more common in ?
More common in the elderly and immunocompromised
What is it reffered to as if patients experience pain due to shingles for greater than 4 weeks
Post herpetic neuralgia
Post herpetic neuralgia affects nerve fibers and skin, causing burning pain that lasts long after the rash and blisters of shingles disappear.
What is herpes zoster ophthalmicus ?

- Herpes zoster ophthalmicus (HZO) describes the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus in the area supplied by the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve.
What are the clinical features of herpes zoster ophthalmicus ?
- vesicular rash around the eye, which may or may not involve the actual eye itself
- Hutchinson’s sign: rash on the tip or side of the nose. Indicates nasociliary involvement and is a strong risk factor for ocular involvement
What is the management of herpes zoster ophthamicus ?
PO aciclovir + urgent referral for ophthalmology review +/- topical corticosteroids
What is wrong with this patient ?
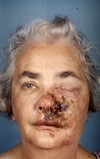
Patient has shingles which is affecting the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve