Viral-Host Cell Interaction, Host Early Defenses Flashcards
Transformation
induces unregulated cellular growth; cells form tumors in susceptible hosts
Permissive Cell
permits production of progeny virus particles and/or viral transformation
Non-permissive Cell
virus cannot replicate, but it may be able to transform the cell
Abortive Infection
no progeny virus particles are produced; however, the cell may die because early viral functions
Interference
Infection by virus A will inhibit second infection with virus B
Persistent Infection
small number of or no virus particles are produced; little or no (cytopatic effects) CPE
Latency
viral genetic material remains in host cell without production of virus; may be activated at a later time to produce virus and/or transform the host cell
Cytopathic Effects (CPE)
- Nucleus: inclusion bodies, thickening of the nucleus, swelling, nucleolar changes
- Cytoplasm: inclusion bodies, vacuoles
One Step Growth Curve
Cells are infected at high multiplicity of infection (MOI) to ensure that every cell is infected. The number of infectious virions inside and outside the cells is measured at various times.

Latent Phase
no virions outside the cells, still inside cell, incubation

Eclipse Phase
no virions outside or inside the cells, the period of time between infection by a virus and the appearance of the mature virus within the cell.

Early Phase
synthetic phase, viral gene expression for genome replication

Late Phase
begins with synthesis of proteins necessary for construction of the new particles
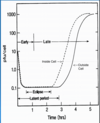
Burst Size
number of infectious virions released per average cell. Range less than 10 to millions. For the figure burst size is 1000.

Interferon
Small proteins produced by cells in response to virus infection, mitogens or immune stimulus.
Three major types of interferon:
- INF-α (Leukocyte) virus induced
- INF-β (Fibroblasts) virus induced
- INF-γ (T-cells) antigen or mitogen induced
How is interferon activated?
- Interferon is activated by double stranded RNA upon viral infection through TLRs.
- Both RNA and DNA viruses induce interferon production.
Interferon activates 2 enzymes:
- Production of an oligoadenylate synthetase which in turn, activates production of ribonuclease that degrades mRNA.
- Production of a protein kinase that phosphorylates and inactivates one of the subunits of initiation factor eIF-2) necessary for protein synthesis.
*The action of both enzymes requires the presence of double stranded RNA

Wait…how is there ds RNA in a DNA virus?
•mRNA folds for stability - this happens in humans as well, but viruses have an increased G + C content –> better interactions –> bigger stems –> induces interferon



