MMR and Other Childhood Exanthems Flashcards
Mumps
- Paramyxovirus genus of the Paramixoviridae family
- ( - ) ss RNA virus
- pleomorphic
Mumps Structure
- (–) Single stranded RNA virus | Nucleoprotein complex
- Matrix protein surrounds nucleocapsid complex
- Envelope contains 2 spikes. One has both H and N activity. The other is called F (fusion) protein.

Mumps Replication
- Replicates in the cytoplasm like (-) RNA viruses by using virion associated RNA dependent RNA polymerase
- Assembles in the cytoplasm
- Buds through cytoplasmic membranes
Mumps Clinical Disease
- Enters respiratory tract
- Replicates in respiratory tract epithelium and local lymph nodes
- Viremia: spreads virus throughout body
- Fever followed by painful swelling of one or both parotid glands (parotitis) usually 12 to 29 days (16–18 days average) after exposure
- Symptoms last 7–10 days
- Immunity is life long

Mumps Incubation Period
- usually 12 to 29 days (16–18 days average) after exposure
- symptoms last 7–10 days
Mumps Common Complications
- Meningitis |Encephalitis (hearing loss)
- Pancreatitis
- Orchitis (10–20% of infected men)
- Oophoritis (inflammation of ovaries)
- Myocarditis (less common)
- 500 cases every year
Mumps Diagnosis
- Clinical picture (most common)
- Isolate virus (saliva, urine)
- Serology
Mumps Treatment
•supportive
Mumps Prevention
•Live attenuated vaccine after 1st year of life or adults (particularly men)
Measles
- Morbillivirus genus of the Paramyxoviridae family
- ( - ) ss RNA
- one antigenic strain
- causes rubeola (5 day measles) and hard measles
Measles Structure
•same as mumps virus but the envelope protein of the measles virus lacks neuraminidase (N) activity
Measles Replication
- same as mumps virus but the envelope protein of the measles virus lacks neuraminidase (N) activity
- Replicates like (-) RNA virus
- Assembles in the cytoplasm
- Buds out from the plasma membrane
Measles Pathogenesis
- Enters respiratory tract and replicates in and destroys mucosal epithelium, necrosis and inflammation
- Spreads to local lymph nodes followed by viremia
- Virus transported to all body organs, conjunctiva, urinary tract, small blood vessels, CNS
- T and B lymphocytes, monocytes, polymorphonuclear leukocytes are infected
- Cell-mediated immunity is depressed by IL-12 downregulation, Natural killer cells impaired
- Enhanced susceptibility to bacterial superinfection
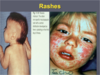
- Skin lesions show vasculitis; vascular dilation, edema and perivascular mononuclear cell infiltrates
- Viral components can be seen in the rash
- In some patients, an immune mediated post infectious encephalitis through CD8 T-cells infiltration in the CNS
Measles Clinical Disease
- Spreads to local lymph nodes
- Viremia: transported to all body organs, symptoms occur 7-18 days (9–11 days average) post exposure
- Koplik spots first appear in mouth (buccal mucosa) as small bluish– yellow spots 1–2 days before rash.
- Rash first appears on head, then trunk and extremities.

Measles Incubation
•symptoms occur 7-18 days (9–11 days average) post exposure
Measles Koplik Spots
•Koplik spots first appear in mouth (buccal mucosa) as small bluish– yellow spots 1–2 days before rash.

Measles Severity
•High fever, delirium, cough, photophobia (light–induced eye pain), conjunctivitis.
Measles Complications
- Encephalitis: death or permanent impairments.
- Bacterial superinfection: otitis media, mastoiditis, pneumonia, sinusitis.
- Death: extensive progressive viral infection.
Measles Epidemiology
- childhood disease; 6 mo. and older. Currently many infections found in teenagers, winter and spring.
- Measles cases have been on rise in US reaching 1250 in 2019
Measles Diagnosis
- Clinical picture (most common)
- Virus isolation (throat, urine), Serology
Measles Prevention
•live, attenuated vaccine after 1st year of life
Measles Treatment
•supportive
Measles - Subacute Sclerosing Pancencephalitis (SSPE)
- Rare, progressive neurologic disease of children, 2 to 10 years after a measles infection
- Insidious onset of personality change, poor school performance, progressive intellectual deterioration, development of myoclonic jerks (periodic muscle spasms), and motor dysfunctions (spasticity, tremors, loss of coordination, ocular abnormalities, blindness)
- Most of the pathologic features of the disease are localized to the CNS and retina
Rubella
- Rubivirus genus of the Togaviridae family
- German or 3 day measles
- ( + ) ss RNA
- one antigenic strain