Vibrational Spectroscopy Flashcards
How many degrees of freedom does an atom have?
3
How many degrees of freedom are there in a diatomic molecule?
6
How many types of motion are there?
Translations - in phase displacements of atoms along cartesian coordinates - no change in internuclear separation or molecular orientation
Rotation: centre of mass is unchanged, no chang ein internuclear separation but orientation change wrt external frame of reference - ot defined
Vibration - a motion of the nuclei in which the centre of mass and orientation remain unchanged but where a change has occurred in internal coordinates - bond length/angle
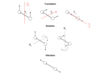
How many degrees of freedom are there for N atoms?
3N
How many vibrations do linear and non-linear molecules have?
Linear: 3 translations, 2 rotation = 3N - 5 vibrations
Non-linear: 3 translation, 3 rotations = 3N - 6 vibrations
What are normal modes of vibration?
The natural vibrations of a molecule
For each normal mode all of the nuclei:
undergo simple harmonic motion
have the same frequency of oscillation
move in phase but generally with different amplitudes
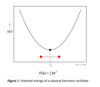
What is Hook’s law and the potential energy if a classical harmonic oscillator?
F = -kx when k = force constat and x is the displacement from equilibria
restoring force - the negative gradient potential energy
How many vibrational modes does water have and what are they?
Non-linear
3N - 6 = (3x3) - 6 = 3
Stretches have higher frequencies than bends
v1 - symmetric stretch is the highest frequency in water

How do we treat each normal mode of vibration?
Each normal mode acts as a harmonic oscillator with vibrational energies
How do we find the vibrational energy levels?
Solve the Schrodinger equation for a harmonic oscialltor

What are the vibrational energies for an anharmonic oscillator?
The anharmonic oscillator levels converge to the dissociation limit De
Experimentally the dissociation energy is measured relatuve to the zero-point
ωe is the spacing that the energy levels would have if the potenial were harmonic with the curvature the actuak curve has at its minimum

How is the actual spacing between a ;pair of energy levels in an anharmonic oscillator calculated?

What are the wavefunctions and wavefunctions squared of a harmionic oscillator?
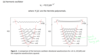
What are the wavefunctions and wavefunction squared of an anharmonic oscillator?

What are some importamt characteristics of normal modes?
In general made up of simultaneous stretching and bending of bonds
Bending vibrations generally lower vrequency than strethches
Heavy atoms move less than lioghter ones
Even at the zero point all normal modes are excited simultaneously
How do we measure IR spectra?
Measure I/I0 - Transmittence where I is the output and I0 is the incident intensity
100% transmittence = no absorption
What happens to the molecule in an IR experiment?
Absorption of an infrared photon promotes a transition from v=0 to v=1
Only photons whose energy exactly match the difference in energy between the two levels will be absorbed
What is the difference between dispersion IR and Fourier transform IR
Dispersion meaures the absorbance of IR radiation as a function of wavelength by dspersing the transmitted light through a monochrometer
A fourier transform instrument measures all IR wavelengths simultaneously using an interferometer with a key advantage being greatly increased speed of meaurement
How do we know if a transition is forbidden or allowed?
The rate of transitions between the initial and final states is proportional to the square of μv’v’’
μv’v’’ = ∫ψ’*vμ^ψ’‘vdx
where x = r-re, μ^ is the electric dipole operator, ψ’*v is the upper vibrational wavefunction and ψ’‘v is the lower vibrational wavefunction
If μv’v’’ = 0 the transition is forbidden
If μv’v’’ ≠ 0 the transition is allowed
What are the selection rules for a transition to be IR active (what allowes μv’v’’ to be non 0)?
It can be shown that
μv’v’’ = (dμ/dx)e ∫ψ’*vμ^ψ’‘vdx + ….
Part 1 (dμ/dx) implies that a transition is allowed only if the dipole moment changes on vibration
Part 2 (the integral) implies that the transition is allowed if it is between adjacent energy levels
Δv = ±1
What do allowed transitions look like for a harmonic oscillator?
All transitions the same energy

How does the selection rule get modified for an anharmonic oscillator?
Δv = ±1, ±2, ±3,…
Δv = + 1 absorption is known as the fundamental absorption
Δv = + 2 = first overtone (second harmonic)
Δv = + 3 = second overtone (third harmonic)
fundamental - v=0 —-> v=1
first overtone - v=0 —> v=2

How would a transition between v=1 and v=2 look in a spectrum?
v=1 —–> v=2 would be close in wavenumber to v=0 —-> v=1 and low intensity - the transition is at a lower energy because most molecules exist in the v=0 state - Boltzmann distribution
This transition is affected by temperature because molecules will only be at higher energy levels at higher tmepratures
These peaks are sometimes called hot bands
How many peaks show up in a specrum if two normal modes are degenerate?
Only 1







