Vesicle transport Flashcards
What does the endomembrane system do?
Name some of its roles
- divides the cell into different membrane bound compartments
- regulates the translation, modification and trafficking of proteins
- turns on/off signal transduction
What are some components of the endomembrane system?
- nuclear envelope
- endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Secretory vesicles
- Endosomes
- Lysosomes
- Autophagosomes
- Plasma membrane

What is a vesicle formed from and what is its function?
- Vesicles bud off of cells and fuse with different compartments
- They carry ‘Cargo’ - cargo is membrane associated soluble molecules
- Each vesicle must be selective for certain cargo and fuse with approproate target membranes

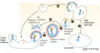
Whats the Secretory pathway?
The flow of membrane bound, and soluble proteins destined for certain organelles or extracellular space flow from ER –> golgi –> plasma membrane via secretory vesicles
Whats the Endocytic pathway?
Plasma membrane capture of extracellular components and internalisation of membrane proteins into vesicles that result in recycling of receptors or degradation of contents in the lysosome
What are the steps of protein transport in the cell?

Why is there a constant bidirectional flow of membrane and proteins?
To ensure integrity of individual organelles i.e. shape/ morphology as well as lipid and protein composition
What pathways are represented by each coloured arrow?


What are the requirements of vesicle transport?
- identification of specific cargo
- Sorting of vesicles and associated cargo
- transport
- Cytoskeletal motor proteins
- transfer of vesticular material
- Fission
- Tethering
- Fusion
The transport vesicles usually have coat proteins that…?
- Provide shape to membranes to “curve” and bud
- Determine the size and shape of the vesicle
- Concentrate the protein in the vesicle
- Provide selectivity for the “cargo”
- Determine the vesicle’s destination
- Coats provide specificity for the destination. Certain coats are only in certain pathways

Name 3 coated vesicles used for vesicle transport?
what locations does each vesicle transport cargo between?
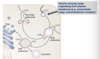
- Clathrin coated vesicles- Trans-Golgi network (TGN) to endosome and plasma membrane (via endocytosis)
- COP I coated vesicles- Golgi complex to the ER (retrieval)
- COP II coated vesicles- ER to golgi

What are the different ways in which proteins associate with the lipid membrane?

What do Clathrin coated vesicles transport cargo between?
Transport material from plasma membrane and between endosomes and Golgi apparatus
What are Clathrin subunits made up of?
3 large (heavy chain) and 3 small polypeptides (light chain) that assemble in ‘triskelions’ at the trans-Golgi network (TGN) or at the plasma membrane

What do Clathrins form?
An outer protein lattice
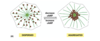
In the following image of a clathrin, what part is the light and heavy chains?
What’s it called when the triskelion structures overlap?

- Red is the heavy chain
- Grey is the light chain
- End terminal globular domain (edge of arm), region which is the distal domain, proximal domain (inside) on heavy chain
- Trimerization domain is interaction and overlap between triskelion structure
Whats Endocytosis?
The englufment of extracellular molecules occuring at the plasma membrane
What does endocytosis regulate?
It regulates receptor signalling, receptor turnover, nutrient uptake, polarity, cell migration and neurotransmission
What are the types of endocytosis and their subtypes if there are any?
- Receptor- mediated endocytosis
- Clathrin-dependent
- Caveolin-dependent (lipid rafts, sphingolipids, GPI anchored proteins)
- Clathrin and Caveolin independent
- Phagocytosis (uptake of large molecules)
- Pinocytosis (uptake of small molecules)

During endocytosis at plasma membrane what recruitment is required?
Recruitment of AP2 adaptor protein complex is required for clathrin recruitment, coat assembly (formation of clathrin-coated pits), and eventual budding
When AP2 adaptor protein binds to a specific phospholipid, what does it result in?
conformational change that allows binding to cargo receptors on cell surface, triggers membrane curvature
What are cargo receptors involved in?
Ligand interactions
Clathrin coat formation diagram

What shape is the AP2 adaptor protein complex?
How many subunits make up the complex?
The AP2 protein complex is a heterotetrameric, multi subunit structure
Its made up of 4 main subunits